Abstrict
Nanogels have been materialized in recent years as a suitable vehicle for the transport and delivery of drug cargo to patients and have been developed as a part of nanomedicines. Nanotechnology drug delivery system has been emerged to fashion their defined field in this interface. By description, nanogels are 3D sub-micron sized cross-linked polymer systems. Nanogels are made of hydrogel particulate constituents with a size range of nanometers; hence, it possesses both hydrogels and nanoparticles' properties. Nanogels have some exceptional properties making them an idea delivery system in various fields including diagnosis, chemotherapeutics, and delivery of genes and targeting specific organs. These ideal properties are stability, better permeation and drug loading ability, responsiveness to environmental stimuli and biologic consistency. This review emphasis chiefly on various types of nanogels, preparation strategies as well as drug loading methods, degradation mechanisms, and drug release mechanisms of drug from nanogels. In this article, we look at these innovative drug delivery systems in more detail with latest pharmaceutical and biological applications of nanogels.
Keywords
Nanotechnology, Nanogels, Macromolecular Network, Cross-Linked
Introduction
Nanogels are basically the nanosized hydrogel, with a diameter of 20-200 nm. Nanogels have been extensively used to increase skin permeation, achieve sustained release effect of drugs, and target targeted drug delivery to the skin's specific area (Yadav, Al Halabi, & Alsalloum, 2017). . Most nanogels are synthesized via some form of the emulsion polymerization reaction. Polysaccharides have been extensively used to prepare nanoparticles and nanogels (Santander-Ortega et al., 2010). However, the exploitation of biodegradable, biocompatible, and non-toxic polymers such as chitin in nanogel form represents a promising concept to influence the controlled and percutaneous drug (Yadav et al., 2017). Prolonging the pharmacological action, sustaining the drug release, decreasing the dose frequency, and reducing the adverse effects of solid particles have been employed in the nanometer range (Kreyling, Semmler-Behnke, & Chaudhry, 2010). However, the biodegradable and biocompatible polymers used in the transdermal and topical drug delivery systems (TDDS) leads to the development of a novel drug delivery system (NDDS). So, several strategies have been discovered so far in the development of nanogels. Among these controlled regeneration chemistry method seems to be more appropriate for the preparation of chitin nanogels (Divya, Panonnummal, Gupta, Jayakumar, & Sabitha, 2016).
Nanogel may be defined as a physically and chemically cross-linked nanosized network or web of particles that show swelling behavior/ effect by using a suitable solvent. The word nanogel was presented to describe the cross-linked bifunctional network of polyion and nonionic polymer for the supply of polynucleotide (cross-linked polyethyleneimine) (PEI), Poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG) or (PEG cl-PEI) (Kabanov & Vinogradov, 2008). Among the arena of nanotechnology, nanogel can convey the drug in a sustained, targeted, and controlled manner to improve the clinical trials and effectiveness of the treatment (Dorwal, 2012). Nanogels show the swelling and degradation property with the flexible size, high surface area, and excellent water content (Hayashi, Iijima, Kataoka, & Nagasaki, 2004). Micro molecules and macromolecules are used to fill pores' opening (Lee, Mok, Lee, Oh, & Park, 2007). Nanogels appear in a three-dimensional network structure in which the drug, dispersed liquid phase, and the polymer are entrapped (Alvarez-Lorenzo, Moya-Ortega, Loftsson, Concheiro, & Torres-Labandeira, 2011).
Classification of Nanogels
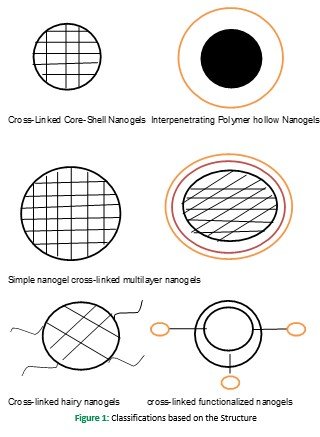
Classification based on the structure is stated as below hollow nanogels (comprising pH and temperature-sensitive nanogels), cross-linked core-shell nanogels are employed mainly to form stimuli-responsive nanogels, functionalized nanogels, hairy cross-linked nanogels, and multilayer nanogel as shown in figure (Sharma et al., 2016)
Classification based on Stimuli Responsiveness
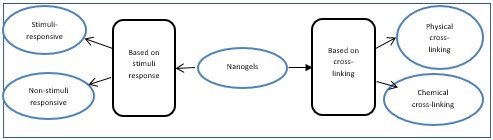
Nanogels are classified into two types
1) Non-responsive nanogels (they got swell upon contact with water by absorbing water)
2) Stimuli-responsive nanogels (These types of nanogels respond to any change in the environmental condition (such as pH, temperature, ionic strength, and magnetic field), acting as stimuli that cause change in response actions of nanogels.
So, if nanogels respond to one or more environmental stimuli, they are termed as multi-responsive nanogels (Sultana, Manirujjaman, Imran-Ul-Haque, & Sharmin, 2013)
Classification based on cross-linking
Nanogels are classified into two types
1) Physically cross-linked nanogels (also referred to as pseudo gel) form weak bonds via i) van der Waals forces ii) hydrogen bonding and iii) hydrophobic and electrostatic interaction. It includes liposomes modified nanogel, micellar nanogel, and hybrid nanogel)
2) Chemically cross-linked nanogels ( In it gel form a covalent bond and the characteristics of cross-linked nanogels rely on the functional group and chemical linkages in the gel network.) (Sultana et al., 2013).
Characteristics and Advantages of Nanogels
Biocompatible and biodegradable
Drug delivery system based on nanogel is exceptionally biocompatible and biodegradable because nanogels cannot store in the body organ. Natural and synthetic polymers are used in its preparation, and these polymers are biodegradable, non-toxic, hydrophilic, and stable (Sultana et al., 2013). Nanogels are administered using various oral, nasal, intraocular, pulmonary, and topical (Garg, Singh, & Goyal, 2013).
Swelling Property in Aqueous Medium
Nanogels can swell in the aqueous environment, and the swelling depends upon the two factors i) structure of the nanogels (which includes charge density in case of polyelectrolyte gel and chemical nature along with cross-linking degree of the polymer chain ii) Environmental parameters( pH, temperature, ionic strength, and chemical nature) (Kabanov & Vinogradov, 2009). Osmotic pressure exerted by the medium ion results in swelling of nanogels. The swelling pressure causes the imbalance of the polymer network (Kazakov & Levon, 2006).
Maximum Drug Loading Ability
Nanogels have higher loading capability related to conventional drug delivery system due to their swelling behavior. However, loading takes place through three methods a) physical entrapment b) controlled self-assembly c) the covalent attachment of bioactive molecules (Kabanov & Vinogradov, 2009).
Particle Size and Permeability
Nanogels, due to their tiny size (20 -200nm), can cross BBB and improve permeability. Permeation occurs through the tissues and the compromised area of endothelium by diffusion mechanism. Due to small size, nanogels can avoid rapid clearance mechanism (Yadav et al., 2017).
Non-Immunological Response
Mononuclear phagocytosis system used opsonization and phagocytosis to eliminate any agent from the systemic circulation. To prolong the stay in blood circulation, there should be a decrease in protein binding. So, hydrophilic polymers act as a shield to hinder binding with opsonin and remain unnoticeable by the immune system and defenses (Gonçalves, Pereira, & Gama, 2010).
Colloidal Stability
Colloidal stability is the main parameter in avoiding the aggregation of particles in the bloodstream to avoid further complications. So, considerable zeta potential causes the repulsion between the particles and electrostatically stabilizes them. Surface modifiers are used to form stable nanosuspension (Sultana et al., 2013). The stability comparison between the polymeric micellar nanogel and surfactant micelles system reveals that the former shows more stability at low critical micelle concentration (LCMC) (S. V. Vinogradov, 2010).
Drug Loading and Drug release Mechanism
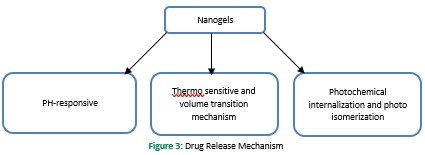
Drug loading in nanogels is performed using nanoprecipitation, solvent evaporation/displacement, direct dissolution, and dialysis. The drug can be integrated into nanogels through covalent bonding, physical entrapment, and self-assembly (Sultana et al., 2013). However, there is a difference in the encapsulation efficiency between each specific nanosystem. Physical drug loading can also be performed by using two ways 1) by incorporating the drug during the preparation of nanoparticles 2) by incubating the concentrated drug solution with the already formed nanocarriers (Gonçalves et al., 2010). Various methods are used in the drug release mechanism, e.g., simple diffusion, pH and temperature change, degradation of nanogel structure, and counterion displacement due to induced energy sources (Kabanov & Vinogradov, 2009). However, in a nanogel system, the drug release is performed by three main mechanisms 1) pH-responsive mechanism 2) thermo-sensitive and volume transition mechanism 3) photochemical internalization and photoisomerization (Yadav et al., 2017).
Preparation Techniques for Nanogels
There is a variety in the techniques and materials used for the preparation of nanogel. Both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs can be used (Garg & Goyal, 2014). However, the choice of method and material relies on various factors such as drug release profile, size, charge, toxicity, stability, and permeability characteristics of the polymers (Chacko, Ventura, Zhuang, & Thayumanavan, 2012).
Nanogels can be prepared by using four methods
1) physical self-assembly of interactive polymer
2) Polymerization of monomer in a homogeneous phase or heterogeneous environment
3) Cross-linking of preformed polymer
4) Template-assisted nanofabrication of nanogel particles (Kabanov & Vinogradov, 2009).
Physical Self-Assembly of Interactive Nanogel
Several research groups have used physical self-assembly of polymer in producing the nanogels. This method involved controlled aggregation of the hydrophilic polymer that contains side groups capable of forming electrostatic and hydrophobic interaction. Hydrogen bonding with each other is occasionally monitored via covalent (e.g., disulfide) bond formation. Appropriate choice of the polymer concentration and environmental parameters such as (pH, ionic strength, and temperature) are used in controlling the size of nanogels. The preparation of nanogels is conducted in aqueous media and mild conditions. For example, hydrogel preparation by the hydrophobic association of cholesterol-modified pullulan in insulin presence (Akiyoshi et al., 1998). Protein nanogels were prepared using temperature-induced gelation of oppositely charge proteins such as ovalbumin and ovotransferrin or lysozymes (Yu, Yao, Jiang, & Zhang, 2006).
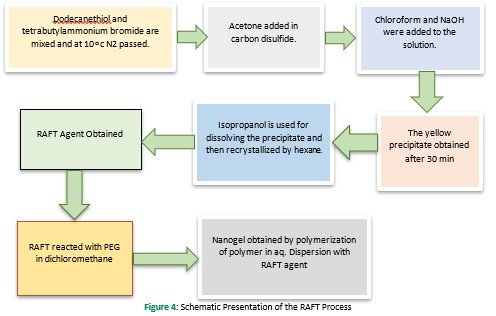
Both hydrophobic and hydrophilic (amphiphilic block copolymer) can synthesize nanogels by the self-associated polymerization technique. So, to synthesize amphiphilic polymers controlled/living radical polymerization techniques( such as nitroxide-mediated polymerization and reversible-addition fragmentation chain transfer techniques) are used (Sharma et al., 2016). However, micellization of the amphiphilic polymer can be modified by altering or changing the nature, length, and composition (Booth & Attwood, 2000; Zamurovic et al., 2007). RAFT process Figure 4 involved a facile method of PEGylated poly (N,N dimethylaminomethylmethacrylate ) nanogel with amphiphilic macro-RAFT agent tri-thiocarbonate with hydrophobic do-decyl chain supporting polymerization. This process is most commonly used for gene delivery due to small particle size (Yan & Tao, 2010). To alter the micellar performance of the amphiphilic block copolymer, a variation in temperature and accumulation of solvent or additives provides an extra degree of freedom (Denkova, Mendes, & Coppens, 2008).
Monomer Polymerization
It is used for the preparation of large particle size nanogels. For the delivery of polynucleotide, Cross-linked cationic nanogels were used to deliver the polynucleotide (Kohli, Han, Zeman, & Vinogradov, 2007). Nanogels have been prepared using various methods such as Carbodiimide coupling, Michael reaction, and free radical polymerization. Carbodiimide coupling involved novel pullulan chemistry modification while heterogeneous free radical polymerization includes a) inverse mini emulsion b) inverse microemulsion polymerization c) precipitation polymerization d) dispersion polymerization utilizing an uncontrolled free radical polymerization.
Chemical synthesis in a heterogeneous
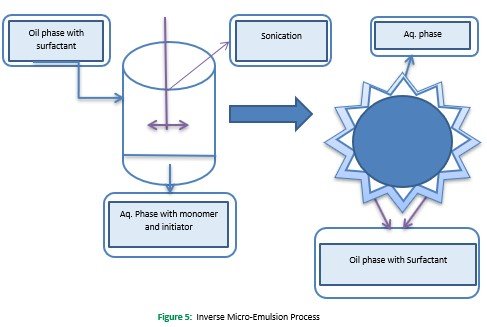
environment can allow changes in the structure and properties of nanogels. However, in the inverse mini emulsion (W/O) polymerization process, aqueous droplets are stably dispersed in the continuous organic environment with oil-soluble surfactants' help (Sultana et al., 2013). However, in the inverse mini emulsion process, mechanical stirring was used to make the stable dispersion, while sonification was done in inverse mini emulsion polymerization. With the addition of a radical initiator within the aqueous droplet, polymerization occurs, producing colloidal particles. An inverse mini emulsion is used to produce kinetically stable macro emulsion at below or above CMC.
In contrast, the inverse microemulsion process is used to synthesize thermodynamically stable microemulsion, which requires more addition of emulsifier beyond the critical threshold. The aqueous droplets continually dispersed in the continuous organic phase throughout the process by using a large number of soluble oil surfactants (Sultana et al., 2013). Cationic PAETMAC nanogels were prepared using inverse microemulsion polymerization of 2-acryloxyethyltrimethylammonium chloride 2-hydroxyethylacrylate in heptane with PEG-bisacrylate was used as a bifunctional cross-linker (McAllister et al., 2002; Sahiner, Godbey, McPherson, & John, 2006) Figure 5.
Cross-Linked Performed Polymer
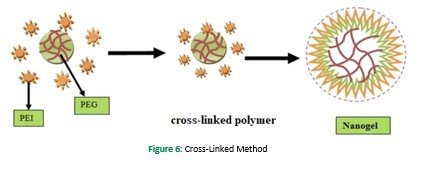
Covalent cross-linking of the preformed polymer provides a unique chance for generating large pore size functional nanogel for drug delivery. A large variety of functional nanogels has been produced by using this technique. This process has been utilized to produce the first cross-linked cationic nanogels for delivering polynucleotide (S. Vinogradov, Batrakova, & Kabanov, 1999). Using this method, nanogel was synthesized by O/W emulsion followed by solvent evaporation, and PEG was conjugated to polyethyleneimine in aqueous media (Sun et al., 2005). Photo-Fenton reaction was used to obtain cationic PEI having a diameter in the range of (80-200nm) in aqueous media (Xu et al., 2007). For the preparation of cationic nanogels, PEIs were connected with the disulfide linkers, whereas hyaluronic acid nanogels, which contain biodegradable disulfide linkages, were synthesized W/O emulsion method (Lee et al., 2007). By mixing thiol-functionalized six-arm branched PEG and DMSO containing DNA by the oxidation process, DNA cross-linked nanogels were prepared (Mok & Park, 2006). Hence, the polymer distribution in nanogel formation can be controlled by both the self-assembled and cross-linked method. Chemically cross-linked nanoparticles have various morphology types, such as rods, spheres, and toroids (Ma, Remsen, Kowalewski, & Wooley, 2001). To control the particle size, morphology, surface characteristics, and composition of the nanogels cross-linking method is applied because it also provides better entrapment of drug within the formulation. Copolymerization technique conducted by using vinyl monomers, e.g., PEG tri-acrylate, PEG monomethyl ether monomethacrylate, and ?-hydroxy styrene (Gratton et al., 2007) Figure 6.
Template-Assisted Nanofabrication of Nanogel Particles
Desimone and coworker developed an innovative method for polymeric particles with a size range of 10nm to several micrometers for the construction of nanogels. (Rolland et al., 2005). Photolithography technique has been used discovered to fabricate the nanogels ring for drug delivery. Photolithography required a technique for surface treatment of new material and stamp for replica mold to allow the molded gel release from replica mold or stamp (Akiyoshi, Sasaki, & Sunamoto, 1999; Oh, Drumright, Siegwart, & Matyjaszewski, 2008).
The following steps are involved in the synthesis of nanogel through this technique.
I. UV cross-linked polymer possessing low surface energy is released on the pre-baked photo-resist-coated water as a substrate.
II. Polymers are molded in a pattern on silicon-wafers by pressing the quartz template onto the polymer or exposing it to intense UV light.
III. By removing the quartz particles with the open thin residual interconnecting film.
IV. The plasma containing oxygen is used to remove the residual film by the oxidation process.
V. The last step involved collecting the fabricated particles through substrate dissolution in buffer's water (Glangchai, Caldorera-Moore, Shi, & Roy, 2008).
Emulsion Photo-Polymerization Technique
Cationic Dextran nanogels were prepared by using the emulsion photo-polymerization technique. This method involved the emulsification of dextran hydroxyethyl methacrylate with ABIL EM 90 as an emulgent in mineral oil, then the obtained formulation in the acetone: hexane (1:1) followed by centrifugation, lyophilization, and desiccation of precipitates. The photosensitizer meso-tetraphenyl porphine disulfonate was presented in the provision to cause rupturing of endosomal membranes in the cell and discharge of genes in cytoplasm and nuclease. Hence for genetic material accomplished for internalization (Raemdonck, Naeye, Høgset, Demeester, & De Smedt, 2010).
Novel Pullulan Chemistry
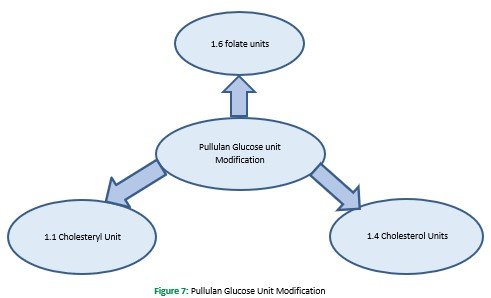
This method is used for self-assembled hydrophobized pullulan nanogels. In this method, modification can occur at various phases: firstly, methacrylates are used, afterthat with hydrophobic, hexadecane thiol. The finished form is always an amphiphilic material, that is by adding water, converted to assemble in hydrophobic interaction between alkyl chain (Ferreira, Coutinho, & Gama, 2011). Cholesterol based pullulan nanogel is another example of this method. Substitution of pullulan occurs at (1.4 cholesterol), and fabrication of nanogels was done by merely reacting cholesterol isocyanate in dimethyl sulfoxide and pyridine. The obtained blend was freeze-dried, and it formed nanogel in the aqueous phase, which then fashioned a complex with the W-9 peptide for delivery in osteological disorder (Alles et al., 2009). Further modification of CHP also occurs with the acrylate group, and their thiol group was modified by adopting Michael's addition reaction. Currently, in the folate receptor targeting system, pullulan has been used, and this system results in the substitution of folate to pullulan by 1.6 glucose units Figure 7. Carbodiimide coupling of pullulan and photosensitizer was done to produce the conjugates that were further converted to nanogel through dialysis in DMSO against deionized water and then used for cancer treatment (Bae & Na, 2010).
Applications of Nanogels
Nanogels have widespread applications in the field of pharmaceutics and bio pharmaceutics. They are mostly employed for the delivery of local anesthetics. Another application is there role as anti-inflammatory vehicle for the delivery of vaccines. Besides, nanogels are used for the delivery of topical and transdermal dosage form, for the delivery of insulin (for diabetic patients), bone marrow regeneration, and in ophthalmology applications. In addition, nanogels have been currently in more practice for the treatment of cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, autoimmune diseases
And microbial infections.
Conclusion
In comparison to other DDS nanogels are being explored as drug delivery agents for various therapeutic and targeting applications. Exceptional properties of nanogels, stability, easy to synthesize and convenient functionalization with cell targeting ligands have opened up opportunities for further development for a variety of biomedical applications, especially drug delivery. Additionally nanogels exhibit improves permeation and retention and have stood up in the field of nanotechnology and TDDS
References
- Akiyoshi, K., Kobayashi, S., Shichibe, S., Mix, D., Baudys, M., Kim, S. W., & Sunamoto, J. (1998). Self-assembled hydrogel nanoparticle of cholesterol-bearing pullulan as a carrier of protein drugs: complexation and stabilization of insulin. Journal of controlled release, 54(3), 313- 320.
- Akiyoshi, K., Sasaki, Y., & Sunamoto, J. (1999). Molecular chaperone-like activity of hydrogel nanoparticles of hydrophobized pullulan: thermal stabilization with refolding of carbonic anhydrase B. Bioconjugate chemistry, 10(3), 321-324.
- Alles, N., Soysa, N. S., Hussain, M. A., Tomomatsu, N., Saito, H., Baron, R., . . . Ohya, K. (2009). Polysaccharide nanogel delivery of a TNF-α and RANKL antagonist peptide allows systemic prevention of bone loss. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 37(2), 83-88.
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C., Moya-Ortega, M. D., Loftsson, T., Concheiro, A., & Torres-Labandeira, J. J. (2011). Cyclodextrin-based hydrogels Cyclodextrins in Pharmaceutics, Cosmetics, and Biomedicine: Current and Future Industrial Applications (pp. 297-321): John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Hoboken, NJ.
- Bae, B.-c., & Na, K. (2010). Self-quenching polysaccharide-based nanogels of pullulan/folate-photosensitizer conjugates for photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials, 31(24), 6325-6335.
- Booth, C., & Attwood, D. (2000). Effects of block architecture and composition on the association properties of poly (oxyalkylene) copolymers in aqueous solution. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 21(9), 501-527.
- Chacko, R. T., Ventura, J., Zhuang, J., & Thayumanavan, S. (2012). Polymer nanogels: a versatile nanoscopic drug delivery platform. Advanced drug delivery reviews, 64(9), 836- 851.
- Denkova, A., Mendes, E., & Coppens, M.-O. (2008). Effects of salts and ethanol on the population and morphology of triblock copolymer micelles in solution. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 112(3), 793-801.
- Divya, G., Panonnummal, R., Gupta, S., Jayakumar, R., & Sabitha, M. (2016). Acitretin and aloe- emodin loaded chitin nanogel for the treatment of psoriasis. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 107, 97-109.
- Dorwal, D. (2012). Nanogels as novel and versatile pharmaceuticals. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, 4(3), 67-74.
- Ferreira, S. A., Coutinho, P. J., & Gama, F. M. (2011). Synthesis and characterization of self- assembled nanogels made of pullulan. Materials, 4(4), 601-620.
- Garg, T., & Goyal, A. K. (2014). Biomaterial-based scaffolds-current status and future directions. Expert opinion on drug delivery, 11(5), 767-789.
- Garg, T., Singh, S., & Goyal, A. K. (2013). Stimuli- sensitive hydrogels: an excellent carrier for drug and cell delivery. Critical Reviews™ in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems, 30(5).
- Glangchai, L. C., Caldorera-Moore, M., Shi, L., & Roy, K. (2008). Nanoimprint lithography based fabrication of shape-specific, enzymatically- triggered smart nanoparticles. Journal of controlled release, 125(3), 263-272.
- Gonçalves, C., Pereira, P., & Gama, M. (2010). Self- assembled hydrogel nanoparticles for drug delivery applications. Materials, 3(2), 1420- 1460.
- Gratton, S. E., Pohlhaus, P. D., Lee, J., Guo, J., Cho, M. J., & DeSimone, J. M. (2007). Nanofabricated particles for engineered drug therapies: A preliminary biodistribution study of PRINT™ nanoparticles. Journal of controlled release, 121(1-2), 10-18.
- Hayashi, H., Iijima, M., Kataoka, K., & Nagasaki, Y. (2004). pH-sensitive nanogel possessing reactive PEG tethered chains on the surface. Macromolecules, 37(14), 5389-5396.
- Kabanov, A. V., & Vinogradov, S. V. (2008). Nanogels as pharmaceutical carriers Multifunctional pharmaceutical nanocarriers (pp. 67-80): Springer.
- Kabanov, A. V., & Vinogradov, S. V. (2009). Nanogels as pharmaceutical carriers: finite networks of infinite capabilities. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 48(30), 5418-5429.
- Kazakov, S., & Levon, K. (2006). Liposome-nanogel structures for future pharmaceutical applications. Current pharmaceutical design, 12(36), 4713-4728.
- Kohli, E., Han, H.-Y., Zeman, A. D., & Vinogradov, S. V. (2007). Formulations of biodegradable Nanogel carriers with 5′-triphosphates of nucleoside analogs that display a reduced cytotoxicity and enhanced drug activity. Journal of controlled release, 121(1-2), 19-27.
- Kreyling, W. G., Semmler-Behnke, M., & Chaudhry, Q. (2010). A complementary definition of nanomaterial. Nano today, 5(3), 165-168.
- Lee, H., Mok, H., Lee, S., Oh, Y.-K., & Park, T. G. (2007). Target-specific intracellular delivery of siRNA using degradable hyaluronic acid nanogels. Journal of controlled release, 119(2), 245-252.
- Ma, Q., Remsen, E. E., Kowalewski, T., & Wooley, K. L. (2001). Two-dimensional, shell-cross-linked nanoparticle arrays. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 123(19), 4627-4628.
- McAllister, K., Sazani, P., Adam, M., Cho, M. J., Rubinstein, M., Samulski, R. J., & DeSimone, J. M. (2002). Polymeric nanogels produced via inverse microemulsion polymerization as potential gene and antisense delivery agents. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 124(51), 15198-15207.
- Mok, H., & Park, T. G. (2006). PEG-assisted DNA solubilization in organic solvents for preparing cytosol specifically degradable PEG/DNA nanogels. Bioconjugate chemistry, 17(6), 1369- 1372.
- Oh, J. K., Drumright, R., Siegwart, D. J., & Matyjaszewski, K. (2008). The development of microgels/nanogels for drug delivery applications. Progress in polymer science, 33(4), 448-477.
- Raemdonck, K., Naeye, B., Høgset, A., Demeester, J., & De Smedt, S. C. (2010). Prolonged gene silencing by combining siRNA nanogels and photochemical internalization. Journal of controlled release, 145(3), 281-288.
- Rolland, J. P., Maynor, B. W., Euliss, L. E., Exner, A. E., Denison, G. M., & DeSimone, J. M. (2005). Direct fabrication and harvesting of monodisperse, shape-specific nanobiomaterials. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 127(28), 10096-10100.
- Sahiner, N., Godbey, W., McPherson, G. L., & John, V. T. (2006). Microgel, nanogel and hydrogel' hydrogel semi-IPN composites for biomedical applications: synthesis and characterization. Colloid and Polymer Science, 284(10), 1121- 1129.
- Santander-Ortega, M., Stauner, T., Loretz, B., Ortega-Vinuesa, J. L., Bastos-González, D., Wenz, G., . . . Lehr, C.-M. (2010). Nanoparticles made from novel starch derivatives for transdermal drug delivery. Journal of controlled release, 141(1), 85-92.
- Sharma, A., Garg, T., Aman, A., Panchal, K., Sharma, R., Kumar, S., & Markandeywar, T. (2016). Nanogel'an advanced drug delivery tool: Current and future. Artificial cells, nanomedicine, and biotechnology, 44(1), 165- 177.
- Sultana, F., Manirujjaman, M., Imran-Ul-Haque, M. A., & Sharmin, S. (2013). An overview of nanogel drug delivery system. J Appl Pharm Sci, 3(8), 95- 105.
- Sun, H., Yu, J., Gong, P., Xu, D., Zhang, C., & Yao, S. (2005). Novel core'shell magnetic nanogels synthesized in an emulsion-free aqueous system under UV irradiation for targeted radiopharmaceutical applications. Journal of magnetism and magnetic materials, 294(3), 273-280.
- Vinogradov, S. V. (2010). Nanogels in the race for drug delivery. Nanomedicine, 5(2), 165-168.
- Vinogradov, S., Batrakova, E., & Kabanov, A. (1999). Poly (ethylene glycol)'polyethyleneimine NanoGel™ particles: novel drug delivery systems for antisense oligonucleotides. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 16(1-4), 291-304.
- Xu, D.-M., Yao, S.-D., Liu, Y.-B., Sheng, K.-L., Hong, J., Gong, P.-J., & Dong, L. (2007). Size- dependent properties of M-PEIs nanogels for gene delivery in cancer cells. International journal of pharmaceutics, 338(1-2), 291-296.
- Yadav, H., Al Halabi, N., & Alsalloum, G. (2017). Nanogels as novel drug delivery systems-A Review. J. Pharm. Pharm. Res, 1(5).
- Yan, L., & Tao, W. (2010). One-step synthesis of pegylated cationic nanogels of poly (N, N′- dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) in aqueous solution via self-stabilizing micelles using an amphiphilic macroRAFT agent. Polymer, 51(10), 2161-2167.
- Yu, S., Yao, P., Jiang, M., & Zhang, G. (2006). Nanogels prepared by self-assembly of oppositely charged globular proteins. Biopolymers: Original Research on Biomolecules, 83(2), 148-158.
- Zamurovic, M., Christodoulou, S., Vazaios, A., Iatrou, E., Pitsikalis, M., & Hadjichristidis, N. (2007). Micellization behavior of complex comblike block copolymer architectures. Macromolecules, 40(16), 5835-5849.
- Akiyoshi, K., Kobayashi, S., Shichibe, S., Mix, D., Baudys, M., Kim, S. W., & Sunamoto, J. (1998). Self-assembled hydrogel nanoparticle of cholesterol-bearing pullulan as a carrier of protein drugs: complexation and stabilization of insulin. Journal of controlled release, 54(3), 313- 320.
- Akiyoshi, K., Sasaki, Y., & Sunamoto, J. (1999). Molecular chaperone-like activity of hydrogel nanoparticles of hydrophobized pullulan: thermal stabilization with refolding of carbonic anhydrase B. Bioconjugate chemistry, 10(3), 321-324.
- Alles, N., Soysa, N. S., Hussain, M. A., Tomomatsu, N., Saito, H., Baron, R., . . . Ohya, K. (2009). Polysaccharide nanogel delivery of a TNF-α and RANKL antagonist peptide allows systemic prevention of bone loss. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 37(2), 83-88.
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C., Moya-Ortega, M. D., Loftsson, T., Concheiro, A., & Torres-Labandeira, J. J. (2011). Cyclodextrin-based hydrogels Cyclodextrins in Pharmaceutics, Cosmetics, and Biomedicine: Current and Future Industrial Applications (pp. 297-321): John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Hoboken, NJ.
- Bae, B.-c., & Na, K. (2010). Self-quenching polysaccharide-based nanogels of pullulan/folate-photosensitizer conjugates for photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials, 31(24), 6325-6335.
- Booth, C., & Attwood, D. (2000). Effects of block architecture and composition on the association properties of poly (oxyalkylene) copolymers in aqueous solution. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 21(9), 501-527.
- Chacko, R. T., Ventura, J., Zhuang, J., & Thayumanavan, S. (2012). Polymer nanogels: a versatile nanoscopic drug delivery platform. Advanced drug delivery reviews, 64(9), 836- 851.
- Denkova, A., Mendes, E., & Coppens, M.-O. (2008). Effects of salts and ethanol on the population and morphology of triblock copolymer micelles in solution. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 112(3), 793-801.
- Divya, G., Panonnummal, R., Gupta, S., Jayakumar, R., & Sabitha, M. (2016). Acitretin and aloe- emodin loaded chitin nanogel for the treatment of psoriasis. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 107, 97-109.
- Dorwal, D. (2012). Nanogels as novel and versatile pharmaceuticals. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci, 4(3), 67-74.
- Ferreira, S. A., Coutinho, P. J., & Gama, F. M. (2011). Synthesis and characterization of self- assembled nanogels made of pullulan. Materials, 4(4), 601-620.
- Garg, T., & Goyal, A. K. (2014). Biomaterial-based scaffolds-current status and future directions. Expert opinion on drug delivery, 11(5), 767-789.
- Garg, T., Singh, S., & Goyal, A. K. (2013). Stimuli- sensitive hydrogels: an excellent carrier for drug and cell delivery. Critical Reviews™ in Therapeutic Drug Carrier Systems, 30(5).
- Glangchai, L. C., Caldorera-Moore, M., Shi, L., & Roy, K. (2008). Nanoimprint lithography based fabrication of shape-specific, enzymatically- triggered smart nanoparticles. Journal of controlled release, 125(3), 263-272.
- Gonçalves, C., Pereira, P., & Gama, M. (2010). Self- assembled hydrogel nanoparticles for drug delivery applications. Materials, 3(2), 1420- 1460.
- Gratton, S. E., Pohlhaus, P. D., Lee, J., Guo, J., Cho, M. J., & DeSimone, J. M. (2007). Nanofabricated particles for engineered drug therapies: A preliminary biodistribution study of PRINT™ nanoparticles. Journal of controlled release, 121(1-2), 10-18.
- Hayashi, H., Iijima, M., Kataoka, K., & Nagasaki, Y. (2004). pH-sensitive nanogel possessing reactive PEG tethered chains on the surface. Macromolecules, 37(14), 5389-5396.
- Kabanov, A. V., & Vinogradov, S. V. (2008). Nanogels as pharmaceutical carriers Multifunctional pharmaceutical nanocarriers (pp. 67-80): Springer.
- Kabanov, A. V., & Vinogradov, S. V. (2009). Nanogels as pharmaceutical carriers: finite networks of infinite capabilities. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 48(30), 5418-5429.
- Kazakov, S., & Levon, K. (2006). Liposome-nanogel structures for future pharmaceutical applications. Current pharmaceutical design, 12(36), 4713-4728.
- Kohli, E., Han, H.-Y., Zeman, A. D., & Vinogradov, S. V. (2007). Formulations of biodegradable Nanogel carriers with 5′-triphosphates of nucleoside analogs that display a reduced cytotoxicity and enhanced drug activity. Journal of controlled release, 121(1-2), 19-27.
- Kreyling, W. G., Semmler-Behnke, M., & Chaudhry, Q. (2010). A complementary definition of nanomaterial. Nano today, 5(3), 165-168.
- Lee, H., Mok, H., Lee, S., Oh, Y.-K., & Park, T. G. (2007). Target-specific intracellular delivery of siRNA using degradable hyaluronic acid nanogels. Journal of controlled release, 119(2), 245-252.
- Ma, Q., Remsen, E. E., Kowalewski, T., & Wooley, K. L. (2001). Two-dimensional, shell-cross-linked nanoparticle arrays. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 123(19), 4627-4628.
- McAllister, K., Sazani, P., Adam, M., Cho, M. J., Rubinstein, M., Samulski, R. J., & DeSimone, J. M. (2002). Polymeric nanogels produced via inverse microemulsion polymerization as potential gene and antisense delivery agents. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 124(51), 15198-15207.
- Mok, H., & Park, T. G. (2006). PEG-assisted DNA solubilization in organic solvents for preparing cytosol specifically degradable PEG/DNA nanogels. Bioconjugate chemistry, 17(6), 1369- 1372.
- Oh, J. K., Drumright, R., Siegwart, D. J., & Matyjaszewski, K. (2008). The development of microgels/nanogels for drug delivery applications. Progress in polymer science, 33(4), 448-477.
- Raemdonck, K., Naeye, B., Høgset, A., Demeester, J., & De Smedt, S. C. (2010). Prolonged gene silencing by combining siRNA nanogels and photochemical internalization. Journal of controlled release, 145(3), 281-288.
- Rolland, J. P., Maynor, B. W., Euliss, L. E., Exner, A. E., Denison, G. M., & DeSimone, J. M. (2005). Direct fabrication and harvesting of monodisperse, shape-specific nanobiomaterials. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 127(28), 10096-10100.
- Sahiner, N., Godbey, W., McPherson, G. L., & John, V. T. (2006). Microgel, nanogel and hydrogel' hydrogel semi-IPN composites for biomedical applications: synthesis and characterization. Colloid and Polymer Science, 284(10), 1121- 1129.
- Santander-Ortega, M., Stauner, T., Loretz, B., Ortega-Vinuesa, J. L., Bastos-González, D., Wenz, G., . . . Lehr, C.-M. (2010). Nanoparticles made from novel starch derivatives for transdermal drug delivery. Journal of controlled release, 141(1), 85-92.
- Sharma, A., Garg, T., Aman, A., Panchal, K., Sharma, R., Kumar, S., & Markandeywar, T. (2016). Nanogel'an advanced drug delivery tool: Current and future. Artificial cells, nanomedicine, and biotechnology, 44(1), 165- 177.
- Sultana, F., Manirujjaman, M., Imran-Ul-Haque, M. A., & Sharmin, S. (2013). An overview of nanogel drug delivery system. J Appl Pharm Sci, 3(8), 95- 105.
- Sun, H., Yu, J., Gong, P., Xu, D., Zhang, C., & Yao, S. (2005). Novel core'shell magnetic nanogels synthesized in an emulsion-free aqueous system under UV irradiation for targeted radiopharmaceutical applications. Journal of magnetism and magnetic materials, 294(3), 273-280.
- Vinogradov, S. V. (2010). Nanogels in the race for drug delivery. Nanomedicine, 5(2), 165-168.
- Vinogradov, S., Batrakova, E., & Kabanov, A. (1999). Poly (ethylene glycol)'polyethyleneimine NanoGel™ particles: novel drug delivery systems for antisense oligonucleotides. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 16(1-4), 291-304.
- Xu, D.-M., Yao, S.-D., Liu, Y.-B., Sheng, K.-L., Hong, J., Gong, P.-J., & Dong, L. (2007). Size- dependent properties of M-PEIs nanogels for gene delivery in cancer cells. International journal of pharmaceutics, 338(1-2), 291-296.
- Yadav, H., Al Halabi, N., & Alsalloum, G. (2017). Nanogels as novel drug delivery systems-A Review. J. Pharm. Pharm. Res, 1(5).
- Yan, L., & Tao, W. (2010). One-step synthesis of pegylated cationic nanogels of poly (N, N′- dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) in aqueous solution via self-stabilizing micelles using an amphiphilic macroRAFT agent. Polymer, 51(10), 2161-2167.
- Yu, S., Yao, P., Jiang, M., & Zhang, G. (2006). Nanogels prepared by self-assembly of oppositely charged globular proteins. Biopolymers: Original Research on Biomolecules, 83(2), 148-158.
- Zamurovic, M., Christodoulou, S., Vazaios, A., Iatrou, E., Pitsikalis, M., & Hadjichristidis, N. (2007). Micellization behavior of complex comblike block copolymer architectures. Macromolecules, 40(16), 5835-5849.
Cite this article
-
APA : Noreen, S., Pervaiz, F., & Shoukat, H. (2021). An Updated Review of Novel Nanogels as Versatile Nano-Platforms for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VI(I), 17-26. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2021(VI-I).03
-
CHICAGO : Noreen, Sobia, Fahad Pervaiz, and Hina Shoukat. 2021. "An Updated Review of Novel Nanogels as Versatile Nano-Platforms for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VI (I): 17-26 doi: 10.31703/gpsr.2021(VI-I).03
-
HARVARD : NOREEN, S., PERVAIZ, F. & SHOUKAT, H. 2021. An Updated Review of Novel Nanogels as Versatile Nano-Platforms for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VI, 17-26.
-
MHRA : Noreen, Sobia, Fahad Pervaiz, and Hina Shoukat. 2021. "An Updated Review of Novel Nanogels as Versatile Nano-Platforms for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VI: 17-26
-
MLA : Noreen, Sobia, Fahad Pervaiz, and Hina Shoukat. "An Updated Review of Novel Nanogels as Versatile Nano-Platforms for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VI.I (2021): 17-26 Print.
-
OXFORD : Noreen, Sobia, Pervaiz, Fahad, and Shoukat, Hina (2021), "An Updated Review of Novel Nanogels as Versatile Nano-Platforms for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications", Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VI (I), 17-26
-
TURABIAN : Noreen, Sobia, Fahad Pervaiz, and Hina Shoukat. "An Updated Review of Novel Nanogels as Versatile Nano-Platforms for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review VI, no. I (2021): 17-26. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2021(VI-I).03
