01 Pages : 1-8
Abstrict
Drug-drug interactions (DDIs) have a considerable impact on therapeutic response which, in turn, could result in adverse drug reactions (ADRs), or even treatment failure. It was directed at patients with cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) as this patient group is more likely to experience DDIs owing to the complexity and number of their drug treatments. The study, analyzed 108 prescriptions using different analytical tools which was carried out for two weeks in Muzaffarabad and Peshawar, Pakistan. The correlation between the number of prescribed drugs and DDIs is significant. There were DDIs in 68.51% of the total number of prescriptions (74/108), including serious interactions in 15.35%. Preservations of prescription practice have to be developed since the results are beginning to underline this last point, especially in a poly-pharmacy environment.
Keywords
Cardiovascular Diseases, Drug-drug Interactions (DDI’s), Poly-pharmacy
Introduction
When the presence of one drug alters the effects of another, this is known as a drug-drug interaction (DDI). Therapeutic failure or unfavorable drug reactions may result from these interactions, which can intensify or lessen the effects of one or both medications (Das et al., 2019). The complexity of drug therapy emerged as a patient's incidence of multiple disease states increased. This increases the possibility of adverse drug reactions, hypersensitivity, unusual reactions, and drug-drug interactions (DDIs). The medication-related problems that still present a major challenge in clinical practice are reactions. Drug-drug interactions (DDI's) may impact the overall therapeutic response through pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic effects. It is estimated that DDIs cause 6 to 30% of all adverse drug reactions (ADRs); 2.8% of these ADRs result in hospital admissions each year.
Globally, cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of mortality. A recent survey indicates that it will account for 20.5 million deaths in 2021.(Di Cesare et al., 2024) Elevated blood pressure, obesity, high blood sugar, smoking, physical inactivity, a family history of heart disease, ethnic background, and other factors are among the numerous risk factors associated with CVDs.(Shah et al., 2018) The more risk factors there are, the higher the chance of developing CVDs. Patients with cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are more susceptible to drug-drug interactions (DDIs) because of the range and quantity of medications they take, as well as the impact of heart disease on drug metabolism.(Kalash et al., 2023) Several investigations carried out worldwide have indicated the heightened presence of these drugs in drug-related dominance incidents.
Even though a patient has multiple disease states, prescriptions are written as though they only have one, and the combined effect of multiple clinical guidelines is not taken into account. Therefore, evaluating the prescription pattern and drug-drug interactions was the aim of this study (Niu et al., 2019) Cardiologists with a sample of patients from various communities, areas, and regions can determine the proportion of patients who have serious and meaningful interactions. Drug interactions have the following types (Drug Interactions: For Drugs, Vitamins, Types, Side Effects & Chart, 2022).
Contraindicated interactions
A combination of two drugs that shouldn't be taken together can have serious or even fatal side effects. Due to the substantial hazards involved, these drug pairs should never be used together under any circumstances.
Serious interactions
Serious drug interactions can cause serious health problems and need to be addressed right away. A healthcare provider must regularly monitor patients for these interactions, and in order to prevent side effects, other medication options may be explored.
Significant interactions
Significant medication interactions may result in perceptible health changes that require attention. Even though these interactions are not as dangerous as those that are contraindicated or serious, they still need to be closely watched and may need dosage modifications for the safety of patients.
Minor interactions
Minor drug interactions usually don't result in harm or obvious side effects. Due to their small effects, these interactions are frequently not significant and don't usually call for adjustments to therapy or monitoring.
Aim of the study
The aim of this research is to assess the prescription
pattern along with DDI among patients suffering from cardiovascular diseases. One aspect is the assessment of disparity in frequency pertaining to relevant and severe DDIs, while another one focuses on the correlation between DRP-a score values and triggers of DDI. This study will enlighten the importance of cautious medication management among CVD patients.
Methodology
Patients with a range of cardiovascular problems were included in this randomized observational study. Over the course of two weeks, 108 prescriptions from patients were chosen randomly across the two cities of Pakistan Muzaffarabad and Peshawar. These prescriptions, which were written by different physicians, entailed both non-cardiovascular and cardiovascular drugs. Information was gathered from heart patients in different areas. Microsoft Office, Microsoft Excel 2013, and the Medscape Drug-Drug Interaction Checker (Drug Interactions Checker, n.d.) were used to conduct the evaluation. Python was used in Google Colab to conduct the data analysis. Pandas and Numpy were used to manipulate data. Data were graphically represented using Matplotlib and Seaborn for univariate and multivariate analysis. Then, employing the SciPy library, we ran statistical tests like ANOVA and t-tests to determine the relationships between various predictors. Then, using the Scikit-Learn library, we put the Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression model into practice to evaluate the relationship between the number of drugs and drug-drug interactions (DDIs). Next, we analyzed the outcomes.
Results:
Prevalence of cardiovascular diseases in age groups
In this research, 108 patients ranging in age from 30 to 90 years are included. There are 34 patients in the 40–50 age group, with 22.22% females and 9.26% males. With 32 patients, the 50–60 age group is the second largest, with a 16.67% male and a 12.96% female patient population. 20 patients in the 60–70 age group are comprised of 8.3% males and 10.18% females. There are 12 patients in the 70–80 age group, with 96.26% males and 1.82% females. Eight (8) patients in the 30-40 age group are male (4.63%) and female (2.77%). There are two patients in the 80–90 age group, with one male (0.926%) and one female (0.926%). The patient's average age is 56.23 years, with an 11.26 standard deviation. Patients' minimum and maximum ages are 35 and 90 years, respectively. A one-way ANOVA test yielded a p-value of 0.579 for the age groups, indicating no significant correlation between the number of drug-drug interactions (DDI's) and age group.
Prevalence of cardiovascular diseases in gender
This study includes 108 patients in total, both male and
female. The gender distribution is 53 for men and 55 for women. There are somewhat more females than males in the population. Regarding other age groups, the age group 40–50 has the greatest proportion of females (24) and the age group 50–60 has the highest proportion of males (18). There is no significant correlation between gender and the number of drug-drug interactions (DDI's), according to the t-test's computed p-value of 0.81.
Drugs Prescribed
About 593 medications, including identical medications, have been prescribed to various patients. Compared to other patients, 23 patients are receiving five medications. Three patients, on average, are being treated with eleven different drugs. The mean number of prescribed drugs is 5.54 with a standard deviation of 2.23. The minimum and maximum number of prescribed medications are 2 and 11, respectively. To determine the relationship between the number of drugs and drug-drug interactions (DDI's), an Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression model is implemented. A significant correlation between the number of drugs and the number of DDI's is shown by the p-value of 0.00. It demonstrates how an increase in drugs could lead to an increase in DDI's. The coefficient for the number of drugs is 0.7488, indicating that the number of DDIs will rise by 0.7488 for every additional drug prescribed. The model's R-squared value of 0.246 suggests that it is a moderate fit.
Drug-drug interaction analysis
There are a total of 293 DDI’s observed in this study, randomly distributed among patients. Out of 108 prescriptions, 31.48% are without DDI's, and 68.51% are with DDI’s. Out of 293 DDI’s, 84.64% are significant, and 15.35% are serious. There are 1-2 DDI’s observed in 34 prescriptions. The mean value for the number of DDI’s is 2.71, and the standard deviation for the number of DDI’s is 3.36. The minimum and maximum values for the number of DDI’s are 0.0 and 17, respectively.
Poly-pharmacy analysis
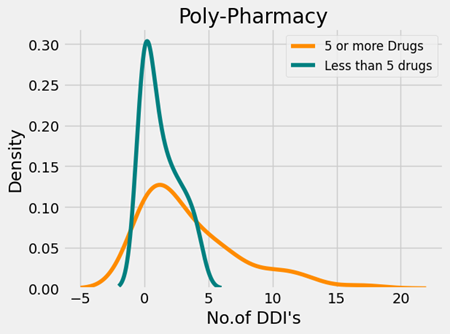
The term "Poly-Pharmacy" refers to five or more drugs per prescription. It has already been well known that an increase in the number of drugs may likely increase the number of DDI's. To get further information, we build a distribution plot of drugs less than 5 and equal to or more than 5. The teal curve is taller and narrower, indicating that most of the prescriptions with less than 5 drugs have a low number of DDIs (0-1). The orange curve, which is shorter and wider, indicates a diverse distribution of DDIs in prescriptions with equal or more than five drugs. It means that with an increase in the number of drugs, it is likely to increase the number of DDI's. The number of DDIs in both groups (less than five drugs, equal to and more than five drugs) was subjected to a t-test, and the p-value is 0.000027. The data suggests a significant variation in the number of DDIs between the two groups. It implies that the likelihood of drug-drug interactions may rise with poly-pharmacy. Therefore, a physician should encourage the rational use of medications and exercise caution and vigilance when prescribing them to cardiac patients in order to prevent drug interactions.
Discussion
The results showed a high prevalence of DDIs in patients with cardiovascular diseases suggesting that the increased use of multiple drugs represents an important safety issue. Data from the study are reported to indicate that as more medications were prescribed an increasing percentage of patients experienced DDIs. This is of particular worry as therapeutic efficacy must be carefully maintained through rigorous disease management among CVD patients. All two hundred ninety-three DDIs across 108 prescriptions were significant interactions (84.64%) and the remaining 45 were serious interaction profile DDIs (15.35%). We cannot stress that medical doctors have to be prudent in co-prescribing various drugs as DDIs between them are of acute concern.
The models used for statistics in the present study exhibit a limited fit, implying that there are other factors dealing with DDI besides those being evaluated here. Still, the strong association re-emphasizes how closely prescriptions are monitored and managed when it comes to reducing risk with poly-pharmacy use in this CVD population.
Conclusion
This study highlights there is a large burden of potential DDIs in patients with CVDs especially driven by an increased number of prescriptions. The large number of moderate to severe and serious interactions emphasizes the necessity for vigilant medication management in this population. Collectively, this analysis supports the concept of a poly-pharmacy burden and encourages adherence to comprehensive clinical guidelines for managing multiple disease states with concomitant treatments. These findings urge that increasing the awareness of and education on equal opportunities amongst healthcare providers around DDIs to establish individualized patient care should be the main focus areas of this Project.
Limitations
The one limitation of the study is the sample size, with a total of 108 prescriptions and therefore not necessarily representative for all. Finally, the study was completed in only two towns; therefore, this limits the power to extrapolate. The study was also observational, with the potential for introduced biases as it depends on the accuracy of recorded prescriptions and patient histories.
Recommendations
Healthcare providers should know how to detect and treat probable DDIs, mainly in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Efforts should be made to develop and adhere to integrated clinical guidelines that will help minimize the risks of poly-pharmacy. Subsequent studies need to be carried out in larger and more ethnically diverse populations to confirm these results as well as examine factors that may give rise to DDIs.
Table 1
Drug-drug interactions were found during the study. (PPI's=Proton Pump Inhibitors, ARB's=Angiotensin Receptors Blockers)
|
Drugs |
Effect |
Type Of Interaction |
|
? blockers+ Furosemide |
Antagonize each other's effect by maintaining a K+ level |
Significant |
|
?
blockers+ Aspirin |
Hyperkalemia |
Significant |
|
? blockers + Spironolactone |
Hyperkalemia |
Significant |
|
?
blockers+ ARBs |
Hyperkalemia |
Significant |
|
Aspirin+ Clopidogrel |
Increase bleeding risk |
Significant |
|
Aspirin+
Furosemide |
Antagonize each other's effect by
maintaining a K+ level |
Significant |
|
Aspirin+ Spironolactone |
Hyperkalemia |
Significant |
|
Aspirin+
ARB’s |
Hyperkalemia |
Significant |
|
ARB’s + Spironolactone |
Hyperkalemia |
Significant |
|
ARB’s+
Furosemide |
Antagonize each other's effect by
maintaining a K+ level |
Significant |
|
Spironolactone + Digoxin |
Hyperkalemia |
Significant |
|
Furosemide+
Digoxin |
Antagonize each other's effect by
maintaining a K+ level |
Significant |
|
PPI’s + Clopidogrel |
Increased metabolism of clopidogrel and bleeding risk |
Serious |
|
PPI’s+
Digoxin |
Increase in digoxin level due to reduced pH
in stomach and absorption is delayed |
Serious |
|
Clarithromycin+ Moxifloxacin |
Increase in heart rhythm to a dangerous level |
Serious |
|
Clarithromycin+
Clopidogrel |
Clopidogrel level increases due to
decreased metabolism |
Serious |
|
Clopidogrel + PPI’s |
Reduction of Antiplatelet activity leads to MI hospitalization. |
Serious |
Table 2
Descriptive Statistics of
Age, No.of Drugs and No.of DDI’s,
|
Statistic
|
Age (years)
|
No. of Drugs
|
No. of
DDI's |
|
Mean |
56.231481 |
5.54296 |
2.712963 |
|
Std |
11.261220 |
2.23007 |
3.357773 |
|
Min |
35.000000 |
2.000000 |
0.000000 |
|
25% |
47.750000 |
4.000000 |
0.000000 |
|
50% |
55.000000 |
5.000000 |
2.000000 |
|
75% |
65.000000 |
7.000000 |
4.000000 |
|
Max |
90.000000 |
11.00000 |
17.00000 |
Figure 1
Prevalence of cardiovascular diseases in age groups
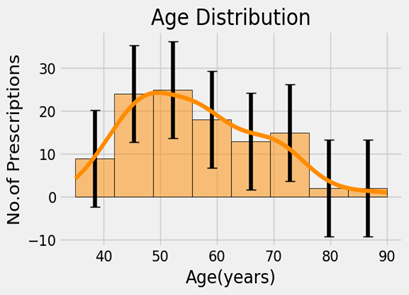
Figure 2
Distribution of age across gender
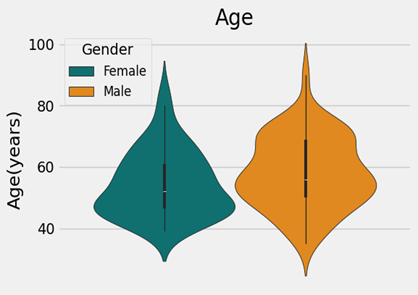
Figure 3
Prevalence of Cardiovascular Diseases in Gender
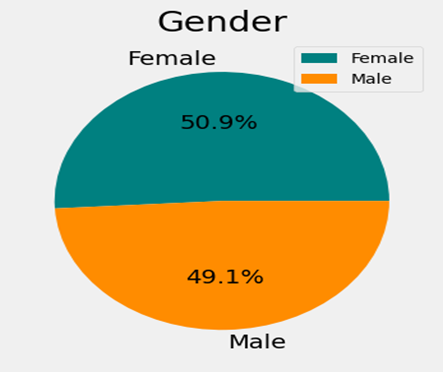
Figure 4
Distribution of drugs prescribed to patients
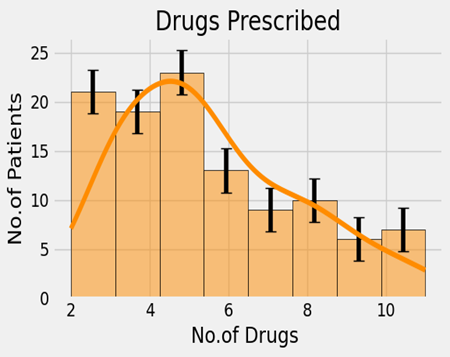
Figure 5
Relationship of No.of drugs to No of drug-drug interactions.
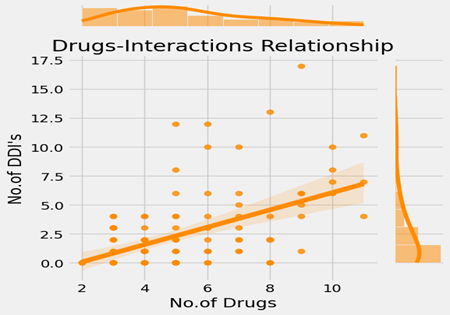
Figure 6
Number of drug-drug interactions in patients
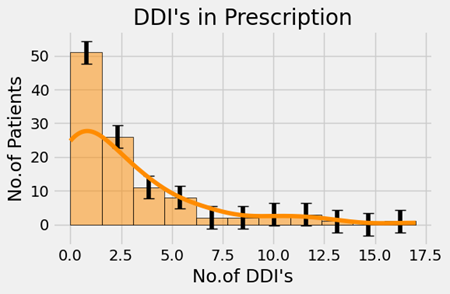
Figure 7
Effect of Poly-pharmacy on Drug-Drug Interactions
References
-
Selvarajan, S., Das, S., Behera, S., Xavier, A., & Dharanipragada, S. (2019). Are drug-drug interactions a real clinical concern? Perspectives in Clinical Research, 10(2), 62. https://doi.org/10.4103/picr.picr_55_18
- Di Cesare, M., Perel, P., Taylor, S., Kabudula, C., Bixby, H., Gaziano, T. A., McGhie, D. V., Mwangi, J., Pervan, B., Narula, J., Pineiro, D., & Pinto, F. J. (2024). The heart of the world. Global Heart, 19(1). https://doi.org/10.5334/gh.1288
- Drug Interaction Checker. (n.d.). https://www.medscape.co.uk/drug-interaction-checker
- PharmD, O. O. (2022, October 19). Drug interactions: for drugs, vitamins, types, side effects & chart. MedicineNet. https://www.medicinenet.com/drug_interactions/article.htm
- Kalash, A., Abdelrahman, A., Al-Zakwani, I., & Suleimani, Y. A. (2023b). Potentially Harmful Drug–Drug Interactions and their associated Factors among hospitalized cardiac patients: a Cross-Sectional study. Drugs - Real World Outcomes, 10(3), 371–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40801-023-00373-3
- Niu, J., Straubinger, R. M., & Mager, D. E. (2019). Pharmacodynamic Drug–Drug interactions. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics/Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 105(6), 1395–1406. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.1434
- Shah, H., Altaf, A., Salahuddin, M., Jan, M. U., & Khan, A. (2018). Cardiovascular risk factors of hypertension, smoking and obesity: Emerging concerns among Pathan and Persian young adults? Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran, 760–764. https://doi.org/10.14196/mjiri.32.129
-
Selvarajan, S., Das, S., Behera, S., Xavier, A., & Dharanipragada, S. (2019). Are drug-drug interactions a real clinical concern? Perspectives in Clinical Research, 10(2), 62. https://doi.org/10.4103/picr.picr_55_18
- Di Cesare, M., Perel, P., Taylor, S., Kabudula, C., Bixby, H., Gaziano, T. A., McGhie, D. V., Mwangi, J., Pervan, B., Narula, J., Pineiro, D., & Pinto, F. J. (2024). The heart of the world. Global Heart, 19(1). https://doi.org/10.5334/gh.1288
- Drug Interaction Checker. (n.d.). https://www.medscape.co.uk/drug-interaction-checker
- PharmD, O. O. (2022, October 19). Drug interactions: for drugs, vitamins, types, side effects & chart. MedicineNet. https://www.medicinenet.com/drug_interactions/article.htm
- Kalash, A., Abdelrahman, A., Al-Zakwani, I., & Suleimani, Y. A. (2023b). Potentially Harmful Drug–Drug Interactions and their associated Factors among hospitalized cardiac patients: a Cross-Sectional study. Drugs - Real World Outcomes, 10(3), 371–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40801-023-00373-3
- Niu, J., Straubinger, R. M., & Mager, D. E. (2019). Pharmacodynamic Drug–Drug interactions. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics/Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 105(6), 1395–1406. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.1434
- Shah, H., Altaf, A., Salahuddin, M., Jan, M. U., & Khan, A. (2018). Cardiovascular risk factors of hypertension, smoking and obesity: Emerging concerns among Pathan and Persian young adults? Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran, 760–764. https://doi.org/10.14196/mjiri.32.129
Cite this article
-
APA : Adnan, M., Saghir, S., & Ahmed, E. (2024). Evaluating Poly-Pharmacy and Drug Interactions in Cardiovascular Treatment: A Call for Vigilant Medication Management. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, IX(II), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2024(IX-II).01
-
CHICAGO : Adnan, Muhammad, Savera Saghir, and Ejaz Ahmed. 2024. "Evaluating Poly-Pharmacy and Drug Interactions in Cardiovascular Treatment: A Call for Vigilant Medication Management." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, IX (II): 1-8 doi: 10.31703/gpsr.2024(IX-II).01
-
HARVARD : ADNAN, M., SAGHIR, S. & AHMED, E. 2024. Evaluating Poly-Pharmacy and Drug Interactions in Cardiovascular Treatment: A Call for Vigilant Medication Management. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, IX, 1-8.
-
MHRA : Adnan, Muhammad, Savera Saghir, and Ejaz Ahmed. 2024. "Evaluating Poly-Pharmacy and Drug Interactions in Cardiovascular Treatment: A Call for Vigilant Medication Management." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, IX: 1-8
-
MLA : Adnan, Muhammad, Savera Saghir, and Ejaz Ahmed. "Evaluating Poly-Pharmacy and Drug Interactions in Cardiovascular Treatment: A Call for Vigilant Medication Management." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, IX.II (2024): 1-8 Print.
-
OXFORD : Adnan, Muhammad, Saghir, Savera, and Ahmed, Ejaz (2024), "Evaluating Poly-Pharmacy and Drug Interactions in Cardiovascular Treatment: A Call for Vigilant Medication Management", Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, IX (II), 1-8
-
TURABIAN : Adnan, Muhammad, Savera Saghir, and Ejaz Ahmed. "Evaluating Poly-Pharmacy and Drug Interactions in Cardiovascular Treatment: A Call for Vigilant Medication Management." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review IX, no. II (2024): 1-8. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2024(IX-II).01
