Abstrict
The research aims to determine the relationship between the mandibular third molars and the nearby lingual cortical bone as well as to determine the frequency of lingual cortex perforation.The analysis was carried out by “CBCTs (cone beam computed tomographic scans)” of 18-65 years old patients. Lingual cortex fenestration at both root tips was observed. Almost three-quarters of radiographs showed the majority of the lingual area on the upper portion of a root (51.2% and 52.8%). The most lingual region and the area surrounding the root tip were both 1.25 mm thick. Mandibular third molars and perforated across both base levels were shown to be significantly related (P value.001). More than 50% of patients had lingual cortical perforation brought on by mandible third-molar teeth. The likelihood of lingual cortical rupture following extraction of the mandibular third molars is a sign of a prior problem rather than surgery.
Keywords
Mandibular Third Molars, Lingual Cortex Perforation, CBCT Scans, Relationship
Methodology
Mandibular 3rd molars or wisdom teeth are the last set of molars to appear in the mouth, usually during the late teens or early twenties. It's important to keep in mind that all wisdom teeth do not need extraction or removal. The decision to extract wisdom teeth depends upon case-to-case situations, keeping in consideration conditions such as the individual's oral health, the position of the teeth, and its potential for complications. Since Mandibular third molar extraction is a routine dental procedure, there are potential complications and risks that can arise and yield a surgical challenge.1 These complications may count Dry socket and/ or infection2, mandibular jaw fracture3, nerve injury4,5, disarticulation of TMJ, root tips displacement to sub-lingual spaces and possibly perforation of lingual cortex6.
Lingual cortex perforation refers to when the extraction instrument or surgical bur inadvertently goes through the lingual cortex instead of staying within the tooth socket.7 This perforation is considered a potential complication of mandibular third molar extraction.8 The lingual cortex is thinner and more delicate compared to the counter buccal cortex, making it more prone to perforation.9 Lingual cortex perforation can be caused by several factors, including the position or angulation of the tooth, proximity of the roots to the lingual cortex, pre-existing perforation because of the roots angulations and the experience and skill of the dental professional performing the extraction10,11. The consequences of lingual cortex perforation can vary depending on the extent and location of the perforation8,12.
In our study, CBCT13,14 data of patients requiring dental surgery were used to evaluate the prevalence of preexisting or pre-surgical lingual plate perforation surrounding mandibular 3rd molars roots.
Methodology
Design and Sampling
Ethical approval was granted for this study by Rehman College of Dentistry, Peshawar. Retrospective data of patients who had gone through CBCT scans were collected from the radiology department of Rahman College of Dentistry between August 2021 and February 2023 having ages of 18 to 65 years. Radiographs showing completely formed impacted and/or nonimpacted mandibular 3rd molars with closed apices were recruited for the study. Bone deformities arising from any localized infection or structural disorders were not included to assure the uniformity of measurements and calculations.15
Variables
To determine the frequency of lingual cortical holes at the base of mandibular third tooth molars that have previously occurred, the Primary outcome variable was too calculated. To gauge the mean width of lingual bone covering the roots of the mandibular 3rd molar, a second outcome variable was calculated.
Demographic variables
This included age & gender. The data was divided into two age groups; 18 - 40 and 41 - 65 years to assess the linkage with age, gender and existence of lingual cortex perforation.
Computed Tomographic Scans (CBCTs) - imaging
With standardized settings of “120 KV'P, 5.0 mA, 0.30 mm slice thickness, and 10,997 m Sec exposure time”, the scans were taken with a Care o Stream 96200 3D' equipment.
Evaluations
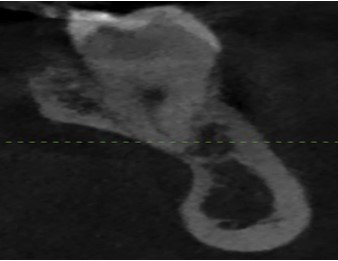
The DPS 360 software was used to analyze the DICOM data. The scan orientation was aligned with the root on the long axis for examination. To keep the depiction of data accuracy, the total volume covering the lingual bone was determined twice from the cross-sectional image. Figure 1 shows the gap between the external border of the lingual cortex and the tooth's root tip for the mandibular third molar. The number 2 denotes the distance between the lingual points located on the apex part of the root and the lingual cortex's outside border. In multi-rooted molars, the most lingual root/position was chosen for assessment. The root perforating lingual cortical plate was designated as zero (Figure.3). Average of these measurements was calculated in mm15.
Statistical analysis
The data was examined using “IBM SPSS for Windows, Version 23.0”. The frequencies of Qualitative data were tabulated in the form of percentages whereas the numerical data was represented by values of mean, median, Standard deviation and other range values. The P value was set as 0.05. Comparisons of qualitative variables were extracted using the Chi-square test.
Discussion
We examined 127 mandibular third-molar teeth from 100 CBCT images, sixty-two per cent of which were men and thirty-eight per cent of which were women. With an average lifespan of 49.8, the ages varied from 18 to 65. About 30% of patients were between 18 to 40 years, while 70% were between the ages of 41 to 65. Impaction was prevalent in 18.1% of cases, and we were able to perform bilateral measurements for 25 radiographs.
In 52.8% of the radiographs, the lingual part was visible on the apical half of the root, and 51.2% of the radiographs indicated lingual cortical rupture at the root apex position (Table 1).
On average, the root apex's lingual bone covering boasted a thickness of 1.25mm, While the bulk of the lingual portion was found with a thickness of 0.96 mm within the upper portion of the root bulb for the group in which there was no perforation (Table 2).
It's significant to note that there was no difference in the prevalence of sublingual cortical perforation between the age categories. With a P value of .001, a highly significant relationship between tongue cortical penetration at the root tip level and the extreme lingual part on the root (upper half) was found. No significant statistics were observed among gender with lingual cortex perforation (Table 4).
Discussion
Achieving satisfaction for both patient and surgeon is the ultimate goal of a successful surgical procedure. Nevertheless, it's important to recognize that complications can arise, sometimes affecting the outcome. One such challenge during third molar surgery is lingual cortex perforation, which may consequence from tooth segment, via a drill or osteotome. Recently, experts have even found signs of surgical lingual perforation roots of certain mandibular 3rd molars.
While panoramic radiography is a popular method for the surgical view of 3rd molars, it struggles to offer a clear picture of the lingual cortical plate due to its 2D nature. Enter CBCT an advanced imagery technique that boasts three-dimensional capabilities, lower radiation doses, and superior spatial resolution compared to CT scans15. This makes CBCT an invaluable diagnostic tool in preparation for third molar surgery. In our study, we employed CBCT to accurately examine theoretical risks in relation to the clinical field16. Although it's premature to advocate for the regular usage of CBCT in preoperative assessments of articulator 3rd molar extractions without substantial-high-quality research evidence, our findings do encourage its use in identifying potential risks associated with a composition that warrants a three dimension perspective for correct evaluation13,14.
Upon delving into the research for comparative studies, we stumbled upon scarce data. Scientists investigated the topographical connection between thirty-two compact mandibular 3rd molar roots and enveloping lingual cortex. Their findings revealed a 12.5% rate of linguistic cortex hole at the base vertex and 15.62% at the apical half's most lingual portion9. Furthermore, Aksoy et al.15 uncovered a 32% perforation incidence across 138 impacted third molars. Intriguingly, these numbers are significantly low in comparison to observations, which could be attributed to differing sample magnitude, mean ages, and a focus on impacted third molars only in these studies, whereas our investigation encompassed both impacted and non-impacted mandibular 3rd molars15.
Our research findings are in close relation with those of Emes et al.28, who discovered that 34.4% of their analyzed data exhibited lingual cortex perforation, specifically in 31 impacted third molars. Adding to this, the lingual cortex covering the root apex was 1.03mm, while it measured around 0.65mm at the majority of the lingual part on the upper one-half of the base – a value marginally smaller than our results. This variation could stem from differing inclusion criteria and measuring software used in each study.
In our intriguing study, we discovered that the most prevalent structure of the lingual cortex surrounding articulator 3rd molars is the undercut form. This finding aligns with reports from Momin et al.,17. The combination of undercut morphology and a thin lingual bone covering can cause vulnerabilities during 3rd molar extraction, potentially increasing the chances of linguistic cortex perforation and base replacing into the sublingual area.
Interestingly, our study found no differences between genders in terms of lingual cortex perforation incidents, which corroborates Parhiz et al.18 findings. Additionally, we observed no mathematics correlation between age groups and lingual cortex perforation incidence. However, Wang et al.8 noted that female patients demonstrated enhanced lingual cortical bony broadness with age. This divergence could be attributed to the prospective nature of our research, making it susceptible to biased selection.
Conclusion
This study reveals that most mandibular 3rd molars whether they've erupted or remained impacted tend to have perforated lingual cortex by their roots, while remaining cases possess a thin layer of lingual cortex. This crucial insight highlights the frequency of lingual cortex perforations before extracting mandibular 3rd molars and alerts us to the commonly thin linguistic cortex, which ups the chances of perforation, harm to the lingual nerve, or root replacement during the release process. Our research underscores the pressing need for precise preoperative imaging of mandibular 3rd molars, along with a thorough discussion with patients about potential risks. In certain cases, using CBCT as a preoperative measure when removing mandibular third molars may be advisable (though not always absolutely necessary). For even more reliable conclusions, we strongly advocate for further research involving larger samples and younger participants on average.
Figure 1
Distance of outer boundary of lingual cortex from the root apex.

Figure 2
Measurement of the Distance from the External Lingual Cortex Boundary to the Lingual Part on the Distal Side of the Root Canal
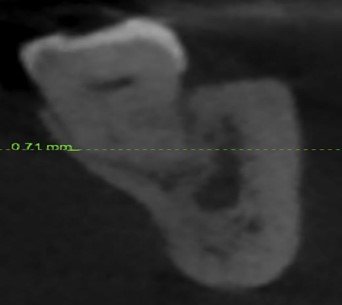
Figure 3
The lingual cortical plate of the root apex.
Tables
Table 1
Incidence and Proportion of Lingual Cortical
Penetration Evaluated at Root Vertex and Lingual Aspect atop the Root to the
Apical Outer Boundary of the Lin
|
|
Dimension |
frequency |
% |
|
Total (n = 128) |
From tip |
64/128 |
52.1 |
|
|
From apex 1/2 |
68/128 |
53.9 |
gual Cortical Plate
Table 2
Prescriptive Data after Measurement for the Mean
Width of the Concealed Lingual bone Assessed at the Point of the Root Plus the Lingual
Section Closest to the Caudal end of its root Towards the Outermost Portion of
the Lingual Cortical Layer
|
|
Dimension(mm) |
Mean |
SD |
95%
CI |
Median |
Range |
|
Total (n = 127) |
From apex |
1.25 |
1.55 |
0.98-1.53 |
0 |
0-5.75 |
|
|
From apical ½ |
0.93 |
1.22 |
0.72-1.15 |
0 |
0-5.36 |
Table 3
Compares the Prevalence of Lingual Cortical
Perforated in Males as well as Females, with the Predictive Data and Results
of the “Chi-square Test and the Fisher's Exact Test”.
|
Flank |
Size (mm) |
n |
% |
|
n |
% |
P value |
Effect size (OR) |
|
Total |
From apex |
20/38 |
52.6 |
|
33/62 |
53.2 |
0.954 |
0.985 |
|
|
From apical 1/2 |
20/38 |
52.6 |
|
35/62 |
56.5 |
0.709 |
0.909 |
References
- Aksoy, U., & Orhan, K. (2018). Risk Factor in Endodontic Treatment: Topographic Evaluation of Mandibular Posterior Teeth and Lingual Cortical Plate Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CT). Medical Science Monitor, 24, 7508–7516. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.908970
- Bataineh, A. B. (2001). Sensory nerve impairment following mandibular third molar surgery. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 59(9), 1012–1017. https://doi.org/10.1053/joms.2001.25827
- Bui, C. H., Seldin, E. B., & Dodson, T. B. (2003). Types, frequencies, and risk factors for complications after third molar extraction. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 61(12), 1379–1389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2003.04.001
- Cankaya, A. B., Erdem, M., Çakarer, S., Çifter, M., & Oral, C. K. (2011). Iatrogenic Mandibular Fracture Associated with Third Molar Removal. International Journal of Medical Sciences, 8(7), 547–553. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.8.547
- D’Angeli, G., Messineo, D., Riminucci, M., Corsi, A., Celli, M., Vozza, I., & Sfasciotti, G. L. (2020). The Characteristics of Adjacent Anatomy of Mandibular Third Molar Germs: A CBCT Pilot Study in Patients with Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Healthcare, 8(4), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8040372
- Emes, Y., Öncü, B., Aybar, B., Al-Badri, N., Issever, H., Atalay, B., & Yalçin, S. S. (2015). Measurement of the Lingual Position of the Lower Third Molar Roots Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 73(1), 13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2014.06.460
- Huang, C. Z., Zhou, C. H., Xu, M., & Zou, D. (2020). Risk factors for lingual plate fracture during mandibular third molar extraction. Clinical Oral Investigations, 24(11), 4133–4142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-020-03286-5
- Jerjes, W., Upile, T., Shah, P. S., Nhembe, F., Gudka, D., Kafas, P., McCarthy, E., Abbas, S., Patel, S., Hamdoon, Z., Abiola, J., Vourvachis, M., Kalkani, M., Al-Khawalde, M., Leeson, R., Banu, B., Rob, J., El-Maaytah, M., & Hopper, C. (2010). Risk factors associated with injury to the inferior alveolar and lingual nerves following third molar surgery—revisited. Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral Pathology Oral Radiology and Endodontology, 109(3), 335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.10.010
- Jing Q, Song H, Huang H, et al. (2023) Characterizations of three-dimensional root morphology and topological location of mandibular third molars by cone-beam computed tomography. Surg Radiol Anat. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-023-03111-0.
- Menziletoglu, D., Taşsöker, M., Kubilay-Isik, B., & Esen, A. (2018). The assesment of relationship between the angulation of impacted mandibular third molar teeth and the thickness of lingual bone: A prospective clinical study. Medicina Oral Patologia Oral Y Cirugia Bucal, 0. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.22596
- Momin, M. A., Matsumoto, K., Ejima, K., Asaumi, R., Kawai, T., Arai, Y., Honda, K., & Yosue, T. (2012). Correlation of mandibular impacted tooth and bone morphology determined by cone beam computed topography on a premise of third molar operation. Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy, 35(4), 311–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-1031-y
- Motamedi, M. R. K., Heidarpour, M., Siadat, S., Motamedi, A. K., & Bahreman, A. A. (2015). Orthodontic Extraction of High-Risk Impacted Mandibular Third Molars in Close Proximity to the Mandibular Canal: A Systematic Review. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 73(9), 1672–1685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2015.03.031
- Parhiz, S. A., Bakhtiary, P., Mosavat, F., & Kharazifard, M. J. (2019). Thickness of Buccal and Lingual Alveolar Bone Plates According to the Position of Impacted Mandibular Third Molars on Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Scans. Frontiers in Dentistry. https://doi.org/10.18502/fid.v16i4.2087
- Peker, I., Sarikir, C., Alkurt, M. T., & Zor, Z. F. (2014). Panoramic radiography and cone-beam computed tomography findings in preoperative examination of impacted mandibular third molars. BMC Oral Health, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6831-14-71
- Tolstunov, L., Brickeen, M., Kamanin, V., Susarla, S. M., & Selvi, F. (2016). Is the angulation of mandibular third molars associated with the thickness of lingual bone? British Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, 54(8), 914–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2016.06.005
- Wagner, K. W., Otten, J., Schoen, R., & Schmelzeisen, R. (2005). Pathological mandibular fractures following third molar removal. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 34(7), 722–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2005.03.003
- Wang, D., He, X., Wang, Y., Zhou, G., Sun, C., Yang, L., Bai, J., Gao, J., Wu, Y., & Cheng, J. (2016). Topographic relationship between root apex of mesially and horizontally impacted mandibular third molar and lingual plate: cross-sectional analysis using CBCT. Scientific Reports, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39268
- Weiss, R. M., & Read-Fuller, A. (2019). Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: An Evidence-Based Review. Dent J (Basel), 7(2), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj7020052
- Aksoy, U., & Orhan, K. (2018). Risk Factor in Endodontic Treatment: Topographic Evaluation of Mandibular Posterior Teeth and Lingual Cortical Plate Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CT). Medical Science Monitor, 24, 7508–7516. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.908970
- Bataineh, A. B. (2001). Sensory nerve impairment following mandibular third molar surgery. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 59(9), 1012–1017. https://doi.org/10.1053/joms.2001.25827
- Bui, C. H., Seldin, E. B., & Dodson, T. B. (2003). Types, frequencies, and risk factors for complications after third molar extraction. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 61(12), 1379–1389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2003.04.001
- Cankaya, A. B., Erdem, M., Çakarer, S., Çifter, M., & Oral, C. K. (2011). Iatrogenic Mandibular Fracture Associated with Third Molar Removal. International Journal of Medical Sciences, 8(7), 547–553. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.8.547
- D’Angeli, G., Messineo, D., Riminucci, M., Corsi, A., Celli, M., Vozza, I., & Sfasciotti, G. L. (2020). The Characteristics of Adjacent Anatomy of Mandibular Third Molar Germs: A CBCT Pilot Study in Patients with Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Healthcare, 8(4), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8040372
- Emes, Y., Öncü, B., Aybar, B., Al-Badri, N., Issever, H., Atalay, B., & Yalçin, S. S. (2015). Measurement of the Lingual Position of the Lower Third Molar Roots Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 73(1), 13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2014.06.460
- Huang, C. Z., Zhou, C. H., Xu, M., & Zou, D. (2020). Risk factors for lingual plate fracture during mandibular third molar extraction. Clinical Oral Investigations, 24(11), 4133–4142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-020-03286-5
- Jerjes, W., Upile, T., Shah, P. S., Nhembe, F., Gudka, D., Kafas, P., McCarthy, E., Abbas, S., Patel, S., Hamdoon, Z., Abiola, J., Vourvachis, M., Kalkani, M., Al-Khawalde, M., Leeson, R., Banu, B., Rob, J., El-Maaytah, M., & Hopper, C. (2010). Risk factors associated with injury to the inferior alveolar and lingual nerves following third molar surgery—revisited. Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral Pathology Oral Radiology and Endodontology, 109(3), 335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.10.010
- Jing Q, Song H, Huang H, et al. (2023) Characterizations of three-dimensional root morphology and topological location of mandibular third molars by cone-beam computed tomography. Surg Radiol Anat. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-023-03111-0.
- Menziletoglu, D., Taşsöker, M., Kubilay-Isik, B., & Esen, A. (2018). The assesment of relationship between the angulation of impacted mandibular third molar teeth and the thickness of lingual bone: A prospective clinical study. Medicina Oral Patologia Oral Y Cirugia Bucal, 0. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.22596
- Momin, M. A., Matsumoto, K., Ejima, K., Asaumi, R., Kawai, T., Arai, Y., Honda, K., & Yosue, T. (2012). Correlation of mandibular impacted tooth and bone morphology determined by cone beam computed topography on a premise of third molar operation. Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy, 35(4), 311–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-1031-y
- Motamedi, M. R. K., Heidarpour, M., Siadat, S., Motamedi, A. K., & Bahreman, A. A. (2015). Orthodontic Extraction of High-Risk Impacted Mandibular Third Molars in Close Proximity to the Mandibular Canal: A Systematic Review. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 73(9), 1672–1685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2015.03.031
- Parhiz, S. A., Bakhtiary, P., Mosavat, F., & Kharazifard, M. J. (2019). Thickness of Buccal and Lingual Alveolar Bone Plates According to the Position of Impacted Mandibular Third Molars on Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Scans. Frontiers in Dentistry. https://doi.org/10.18502/fid.v16i4.2087
- Peker, I., Sarikir, C., Alkurt, M. T., & Zor, Z. F. (2014). Panoramic radiography and cone-beam computed tomography findings in preoperative examination of impacted mandibular third molars. BMC Oral Health, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6831-14-71
- Tolstunov, L., Brickeen, M., Kamanin, V., Susarla, S. M., & Selvi, F. (2016). Is the angulation of mandibular third molars associated with the thickness of lingual bone? British Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, 54(8), 914–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2016.06.005
- Wagner, K. W., Otten, J., Schoen, R., & Schmelzeisen, R. (2005). Pathological mandibular fractures following third molar removal. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 34(7), 722–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2005.03.003
- Wang, D., He, X., Wang, Y., Zhou, G., Sun, C., Yang, L., Bai, J., Gao, J., Wu, Y., & Cheng, J. (2016). Topographic relationship between root apex of mesially and horizontally impacted mandibular third molar and lingual plate: cross-sectional analysis using CBCT. Scientific Reports, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39268
- Weiss, R. M., & Read-Fuller, A. (2019). Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: An Evidence-Based Review. Dent J (Basel), 7(2), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj7020052
Cite this article
-
APA : Khan, M. I., Durrani, Z., & Ullah, U. (2023). Prevalence of Pre-Existing Lingual Cortex Perforation Prior to Extraction of Mandibular Third Molars. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII(II), 50-56. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2023(VIII-II).10
-
CHICAGO : Khan, Muhammad Ihtesham, Zubair Durrani, and Umer Ullah. 2023. "Prevalence of Pre-Existing Lingual Cortex Perforation Prior to Extraction of Mandibular Third Molars." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII (II): 50-56 doi: 10.31703/gpsr.2023(VIII-II).10
-
HARVARD : KHAN, M. I., DURRANI, Z. & ULLAH, U. 2023. Prevalence of Pre-Existing Lingual Cortex Perforation Prior to Extraction of Mandibular Third Molars. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII, 50-56.
-
MHRA : Khan, Muhammad Ihtesham, Zubair Durrani, and Umer Ullah. 2023. "Prevalence of Pre-Existing Lingual Cortex Perforation Prior to Extraction of Mandibular Third Molars." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII: 50-56
-
MLA : Khan, Muhammad Ihtesham, Zubair Durrani, and Umer Ullah. "Prevalence of Pre-Existing Lingual Cortex Perforation Prior to Extraction of Mandibular Third Molars." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII.II (2023): 50-56 Print.
-
OXFORD : Khan, Muhammad Ihtesham, Durrani, Zubair, and Ullah, Umer (2023), "Prevalence of Pre-Existing Lingual Cortex Perforation Prior to Extraction of Mandibular Third Molars", Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII (II), 50-56
-
TURABIAN : Khan, Muhammad Ihtesham, Zubair Durrani, and Umer Ullah. "Prevalence of Pre-Existing Lingual Cortex Perforation Prior to Extraction of Mandibular Third Molars." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review VIII, no. II (2023): 50-56. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2023(VIII-II).10
