Abstrict
Ocular inserts of Pilocarpine nitrate (PN) were prepared using modified karaya gum (MKG) alone as release retarding polymer and in combination with the copolymer sodium alginate. Modification of the karaya gum was done by treating it with the trisodium trimetaphosphate (STMP) by cross linking method and evaluated for its physicochemical properties. Films of the MKG were prepared by employing solvent casting method using varying concentrations (600mg, 500mg and 400mg) of MKG and the sandwiching technique was used for the loading of drug. Sodium alginate (SA) and PN blend were prepared by triturating their appropriate amounts. Six ocusert formulations (F1-F6) were prepared with different concentrations of the polymer i.e MKG and SA while the amount of PN was kept constant in formulations. Formulations F1-F3 contained the MKG alone in varying concentrations (600mg, 500mg and 400mg) and F4-F6 contained SA (0.5 mg) in addition to MKG. The surface pH of prepared ocuserts from the formulations (F1-F6) was in the range of 6.63 to 6.8. Thickness range of the ocuserts was from 0.21 to 0.32 mm. Dissolution profiles of prepared ocuserts were studied and drug release was found within the range of 69.2±1.36 % (F4, minimum) to 90.5±3.21% (F3, maximum). Overall results of the study concluded that ocuserts fabricated with MKG and SA at optimized concentrations have the potential to sustain the release of PN and therefore reducing dosing frequency and adverse effects.
Keywords
Ocuserts, sodium alginate, crosslinking, solvent casting, diffusion
Introduction
Due to advancements in pharmaceutical technology, the novel drug delivery systems are now quickly substituting the conventional dosage forms. Sustained released system of drug delivery is one of the prominent representative of this recent trend and has drawn the concentration of pharmaceutical scientists and researchers. Sustained release system of drug delivery is the system which allows constant and slow release of drug for prolong period of time. Such system can also be known as controlled release system of drug delivery where they release controlled amount of drug at the site of absorption. The controlled release can be time related or spatial (Krishnaiah, Reddy et al., 2002).
Drug delivery through the ocular system is always a challenging field for pharmaceutical researchers. The most important objective of ophthalmic drug delivery is to achieve and maintain the curative drug concentration at the absorption site. Eyes are impermeable to foreign substances due to it's anatomical, physiological and biochemical properties. It is challenging for researchers to develop the dosage form to avoid the barriers without creating permanent harm to the ocular tissues (Sultana, Jain et al., 2006).
There are various precorneal, static and dynamic ophthalmic barriers that cause hindrance in the delivery of drug to the targeted ophthalmic site, so it is difficult to attain therapeutic drug levels at target tissue for longer duration. Conventional dosage forms being used today are ophthalmic solutions, eye drops, and ointments. patient compliant and most suitable drug administration route for the ophthalmic drug delivery is eye drops. The main disadvantages of eye drops are low corneal permeability, tears turn over, blinking and drainage due to gravity. Only 1-10% of the administered drug is absorbed and consequently results in poor bioavailability (Patel, Cholkar et al., 2013).
In the treatment of ophthalmic disease generally, the high concentrations of drug are used because of inadequate ophthalmic bioavailability resulting in unavoidable ocular and systemic side effects. In ocular suspensions, mostly water soluble drugs are used that pose high toxicity due to the saturated solution of water soluble drugs (Rathore and Nema, 2009b).
Now researchers have been focusing towards development of drug releasing devices and nanoformulations for treating ocular diseases. Novel formulations and devices may be helpful to surpass ocular barriers and related side effects occurring with conventional eye drops. These novel formulations and devices are easy to formulate, have high pre-corneal residence time and almost non or negligibly irritating, control the drug release, and enhance ocular bioavailability (Patel, Cholkar et al., 2013)
Material and Methods
PN and STMP were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH. Karaya gum was purchased from the local market. Sodium alginate was received as a gift for research purpose from the Bio Labs Pharmaceuticals, Islamabad, Pakistan. Sodium hydroxide, glycerol, sodium chloride, and methylene blue were purchased from Icon Chemical-Germany, Nimir Chemical-Pakistan, BDH Laboratory Supplier-England and Fluka chemika, Switzerland respectively. Disodium phosphate and Monobasicpotassium phosphate were purchased from Merk, Germany. Double-distilled water was used for the preparation of the inserts and buffer solutions. All chemical materials were of analytical grade and used without further modification.
Modification of KG
Natural KG was modified by cross-linking with STMP using the method described in the literature (Reddy, Reddy et al., 2012). 5g of STMP was accurately weighed and dissolved in water (250ml) and gradually added to a beaker containing 5g of karaya gum in 250ml water and 25ml of 0.1N NaOH while stirring was on. Resulting reaction mixture was further stirred for 2 hours and then transferred into petri dishes, which were dried at 60°C for a period of 24 hours. Modified dried gum was then removed from petri dishes and converted into fine powder by sieving (200 µ sieve). The fine powder was further utilized for development of PN loaded ocuserts
FTIR Spectroscopy
FTIR spectroscopy (IR-Prestige-21, Shimadzu, Japan) was performed on KG and MKG by using the KBr disk method. (Reddy, Reddy et al., 2012).
Determination of ? max of Pilocarpine Nitrate
? max of the PN was determined by scanning the solution of concentration 10µg/ml in phosphate buffer of pH 7.4 between the range of 200-400nm.
Preparation of Calibration Curve of Pilocarpine Nitrate in Phosphate Buffer Saline
For the preparation of calibration curve of Pilocarpine Nitrate, aliquots of 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 and 14ml were taken from the solution of concentration 10µg/ml into the different volumetric flasks and volume was made up to the 100ml with the help of phosphate buffer saline of pH 7.4 to get the drug concentrations 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14µg/ml respectively. The absorbance of these solutions was measured with double beam UV spectrophotometer and the calibration curve was obtained with the help of concentration and absorbance (Anumolu, Vijay Amritharaj et al.).
Development of Ocuserts
Six different formulations of ocular inserts were developed coded as F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, and F6. Formulations (F1 to F3) were prepared using varying amounts of MKG as given in table 1. Glycerol was used as plasticizer in varying concentration 0.1mL, 0.083mL and 0.066mL respectively in F1 to F3. Whereas formulations F4, F5, and F6 contained equal amounts of MKG and glycerol (as F1, F2 and F3), but sodium alginate (0.5 mg) was incorporated into these formulations along with drug between the two films of MKG.
Ocuserts of PN were prepared using the sandwich method (Devhadrao, Siddhaia et al., 2018). The first step involves formation of film of MKG using glycerol as plasticizer, and film was cut into the small circles of 5mm diameter. The second step involves incorporation of PN (1 mg) in between two prepared films and sides were sealed with the paste of MKG.
Composition of different formulations (F1-F6) of ocuserts
|
Formulation |
MKG (mg) |
PN (mg) |
Sodium Alginate (mg) |
Glycerol (ml) |
|
F1 |
600 |
1 |
- |
1 |
|
F2 |
500 |
1 |
- |
0.083 |
|
F3 |
400 |
1 |
- |
0.066 |
|
F4 |
600 |
1 |
0.5 |
1 |
|
F5 |
500 |
1 |
0.5 |
0.083 |
|
F6 |
400 |
1 |
0.5 |
0.066 |
Preparation of MKG Film
For the preparation of the film of MKG, 60ml of distilled water was taken into the 100ml beaker. Accurately weighed MKG as per formulation given in table 3.1 was sieved through the mesh size 120 and added to beaker gradually with constant stirring using hot plate magnetic stirrer (RSM02HP Phoenix Germany). Glycerol was added with stirring. The petri dishes with above solution were allowed to dry at 40°C in oven (Memmert, Germany). A thin film of polymer was removed from the surface of the perti dish before its complete drying. The film was further dried in hot air oven at the temperature 40°C. Separate film for individual formulation was developed. Small circular pieces of 5mm diameter were cut by using sharp edge die from these films.
Sandwiching the PN between the Film and Sealing
1mg of PN was weighed accurately on the piece of the clean butter paper using an analytical weighing balance (Shimadzu ATX 22, Germany).
A previously cut piece of film 5mm in diameter from the first step was placed on a dried, clean and flat glass surface. PN was carefully transferred to the center of the film with the help of micro spatula and applied with paste of the polymer. After drying, ocusert was removed from the oven and sealing paste was again applied on the margins to achieve accurate sealing and dried again. Sterilization was done by placing ocuserts under UV light for few minutes and preserved in airtight glass container for more evaluation
Percentage Drug Contents/ Drug content uniformity
Percentage drug contents evaluation was done with the help of UV/Visible spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV 1601, Japan). Three ocuserts from individual formulation were chosen and dissolved separately in phosphate buffer saline pH 7.4. Solution prepared was then filtered, diluted and checked for PN contents at wavelength of 207.5 nm. The concentration of drug was measured using the standard calibration curve. Three readings for every formulation were taken and standard deviation was determined.
Drug-Excipients compatibility Study by FTIR Spectroscopy
The compatibility of the excipients with drug was established by FT-IR analysis. The FTIR spectra of MKG, PN, SA and STMP individually and in mixture were recorded using a Shimadzu FTIR spectrophotometer (IR-Prestige-21, Shimadzu, Japan). Sample discs were prepared in hydraulic press using the KBr disks technique at the pressure of 10,000 Psi. Scanning was performed in the scanning range of 4,000–400 cm?1 at ambient temperature.
In-Vitro Drug Release Studies
In-Vitro release of drug from the prepared ocuserts was carried out using vial method with some modification. For dissolution studies, each ocusert was placed in a test tube of a capacity 10ml containing 10ml of dissolution medium (phosphate buffer saline pH 7.4). The Temperature was kept constant at 37 ±1°C. These test tubes were placed on a reciprocating shaker and at 37 ± 1°C. In order to simulate the movement produced by the blinking of the eye, the speed of the reciprocating shaker was adjusted to a minimum. 5ml sample from the test tube was withdrawn after specific intervals of time and similar volume was replaced by the fresh dissolution medium. Samples withdrawn were suitably diluted with the dissolution medium and were analyzed at 207.5nm using Shimadzu Double beam Spectrophotometer 1601 UV against blank (Amar, Ashish et al., 2012).
Results
Physicochemical Characterization of MKG
Physicochemical Properties of Modified Karaya Gum (MKG)
|
Sr. No. |
Parameters |
Results |
|
1 |
Swelling Index |
47.5 ± 0.6% |
|
2 |
Loss on Drying |
9.8 ± 0.4% |
|
3 |
Total Ash |
2.8 ± 0.1 |
|
4 |
pH (1% Solution) |
6.8 ± 0.2 |
|
5 |
Bulk Density |
0.613 ± 0.014 |
|
6 |
Tapped Density |
0.791 ± 0.021 |
|
7 |
Compressibility index |
22.58 ± 0.02 |
|
8 |
Hausner's Ratio |
1.291 ± 0.03 |
|
9 |
Angle of Repose |
38.5 ± 1.5% |
Values are expressed as Mean ± SEM (n=3)
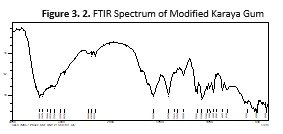
FTIR Spectroscopy
The chemical nature of the MKG was elucidated by recoding FTIR spectra using FTIR Spectrophotometer (IR-Prestige-21, Shimadzu, Japan)in the range of 400 to 4000 cm-1andcompared with the already reported spectra (Reddy, Reddy et al., 2012). New broadened peak appear at 3383cm-1 showed stretching of N-H bond of amide group. The presence of new peaks in the MKG evident the stretching of phosphate-I and bending of phosphate-II. The presence of phosphate groups of the STMP indicated successful modification by cross-linking
|
Peak
(cm-1) |
Group |
Stretching/Bending/Deformation |
|
3383 |
O-H & N-H |
Stretching |
|
2931 |
C-H |
Stretching |
|
1411 |
Ring |
- |
|
1072 |
C-O |
Bending |

Determination of ? max of Pilocarpine Nitrate
The solution of concentration 10µg/ml was scanned between 200-400nm and spectrum obtained, The ? max for Pilocarpine Nitrate was found to be 207.5nm. It was used as an analytical wavelength throughout the study.
Preparation of Calibration Curve of Pilocarpine Nitrate in Phosphate Buffer Saline
The absorbance of the different concentration solutions was noted at the wavelength 207.5nm and the calibration curve obtained shown in figure 3.3

Physicochemical Characterization of Prepared Ocuserts
Physicochemical characterization of prepared PN ocuserts was
carried out and results are as follow:
|
Parameter |
Results |
|||||
|
Thickness
(mm) |
F1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
F6 |
|
0.3±0.01 |
0.255±0.002 |
0.21±0.01 |
0.32±0.01 |
0.26±0.01 |
0.22±0.02 |
|
|
Weight
(mg) |
8.6±0.03 |
7.4±0.03 |
6.2±0.05 |
9.1±0.02 |
7.6±0.01 |
6.6±0.03 |
|
Swelling Index (%) |
33.81±0.10 |
33.35±0.12 |
33.1±0.11 |
36.79±0.20 |
36.7±0.15 |
36.13±10 |
|
Surface pH |
6.74±0.02 |
6.63±0.01 |
6.71±0.012 |
6.64±0.02 |
6.78±0.02 |
6.8±0.01 |
Values are expressed as Mean ± SEM (n=3)
Percentage Drug Contents
Percentage of drug content for the six formulations was determined and observed in the range of 95% to 100% that complies with the pharmacopeial requirements. The results showed the accuracy and reproducibility of the method used to prepare ocuserts.

Values are expressed as Mean ± SEM (n=3)
Drug-Excipients Compatibility Study by FT-IR Spectroscopy
FTIR spectrum of the formulation and PN were recorded and compared. There was no major shifting of peaks were detected. Minor shifting of peaks were observed such as Peaks present at 2920cm-1, 1762cm-1, 1689cm-1, 1215cm-1, 1072cm-1were shifted to 2935cm-1, 1766cm-1, 1608cm-1, 1242cm-1, 1068cm-1 respectively. By comparing the two spectra it was concluded that there was not any significant interaction between the components of the formulation and PN.
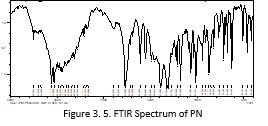

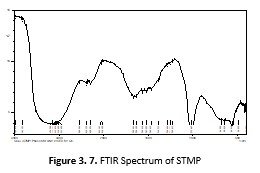


Figure 8
Figure 3. 9. Drug Release Profile of PN from all the six formulation
using Phosphate buffer saline pH 7.4.
Kinetic Modeling
Release data was undergone through kinetic models and shown in table 3.8. All the formulations were best fitted in the Korsmeyer's Peppas model by showing high values of R2. Value of the R2 for the optimized formulation (F4) is of the Korsmeyer's Peppas model was 0.9975. It indicates that the formulation is best fitted in the korsmeyer's peppas model. The Release of drug was through non Fickian diffusion mechanism (n=0.672).
Table 3. 8. Kinetic Modeling of PN ocuserts based on MKG in phosphate buffer saline pH 7.4.
|
Kinetic
Models |
F1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
F6 |
|
|
Zero Order |
R2 |
0.7786 |
0.6147 |
0.4040 |
0.9205 |
0.8168 |
0.6769 |
|
Ko |
8.069 |
9.244 |
9.613 |
6.566 |
7.370 |
8.533 |
|
|
First Order |
R2 |
0.9821 |
0.9725 |
0.9491 |
0.9952 |
0.9829 |
0.9691 |
|
K1 |
0.154 |
0.218 |
0.263 |
0.102 |
0.129 |
0.179 |
|
|
Hixon
Crowell Model |
R2 |
0.9490 |
0.9277 |
0.8840 |
0.9844 |
0.9534 |
0.9216 |
|
KCH |
0.043 |
0.059 |
0.071 |
0.030 |
0.036 |
0.049 |
|
|
Higuchi
Model |
R2 |
0.9923 |
0.9895 |
0.9488 |
0.9654 |
0.9833 |
0.9925 |
|
KH |
23.592 |
27.380 |
28.821 |
18.837 |
21.453 |
25.169 |
|
|
Korsmeyer
Peppas Model |
R2 |
0.9937 |
0.9969 |
0.9917 |
0.9975 |
0.9892 |
0.9942 |
|
Kkp |
22.225 |
31.008 |
37.761 |
13.360 |
18.862 |
26.791 |
|
|
N |
0.530 |
0.436 |
0.361 |
0.672 |
0.565 |
0.468 |
|
Discussion
Ocular inserts of PN were prepared using the natural polymer (KG) by making some modifications in it. Modification of the natural KG was accomplished by cross-linking it with the STMP. Natural KG was selected due to its easy availability, less cost and compromised hypersensitivity reaction showing to natural origin (Prajapati, Jani et al., 2013). After modification, MKG was evaluated for its physicochemical properties that are swelling index, bulk density, tapped density, pH, loss on drying, Hausner's ratio, compressibility index, total ash contents and solubility characteristics.
The modification of karaya gum into MKG was further confirmed using FTIR spectroscopy. The spectra obtained were compared with already reported spectra (Reddy, Reddy et al., 2012). The presence of new peaks in the MKG evident the stretching of phosphate-I (C=O) and bending of phosphate-II (C-O). The presence of phosphate groups of the STMP indicated successful modification by cross-linking.
At first instance, MKG was evaluated for its solubility in aqueous and organic phases. It was found insoluble in water and many organic solvents including chloroform, methyl alcohol and ethyl alcohol at room temperature. Complete solubility was shown in DMSO at 80°C. The hydrophobic nature of the MKG made it a suitable polymer for diffusion-based ocuserts (Siepmann and Peppas, 2000). Cross-linking density of the gum was increased by the modification which ultimately enhances swelling index (Kabiri, Omidian et al., 2003). The swelling index was 47.5±0.6% that makes it an ideal release retarding polymer. Higher swelling index indicated the more gel-forming ability of the polymer that increases the path length of diffusion of drug and ultimately decrease the rate of drug release (Jain, Yadav et al., 2008). pH of the MKG was found approximately neutral similar to the pH of eye that makes it suitable polymer for the ophthalmic preparations. Generally in case of ophthalmic preparations pH approximately kept near to the neutral as the pH of the lacrimal fluid is 7.4 (Gupta and VYAS, 2010, Malhotra and Majumdar, 2001).
UV spectroscopic studies showed ? max of 207.5 nm for PN. The calibration curve for PN was constructed using phosphate buffer saline of pH 7.4 at wavelength 207.5nm (Anumolu, Vijay Amritharaj et al.). Calibration curve is employed to find out drug concentration in an unknown sample with reference to standard and also used to calibrate the instrument Standard curve during research was obtained to analyze the unknown concentrations in different dilutions contained PN (Breeveld, Landsman et al., 2011).
Films of the polymer were prepared with different concentration of MKG i.e. 600mg, 500mg, 400mg by the solvent casting method. The prepared films were used for the preparation of various formulations of ocuserts alone or in combination with the other polymers. Ocuserts were prepared by the sandwich method (Devhadrao, Siddhaia et al., 2018). Six different formulations F1-F6 were prepared, formulations F1, F2 and F3 contained 600mg, 500mg and 400mg of the MKG respectively while the formulations F4, F5, and F6 contain the same amount of MKG with the addition of 0.5mg of Sodium alginate in each. Sodium alginate was used as a copolymer for evaluating its sustained impact on the formulation. Sodium alginate was incorporated into the formulation by triturating it with the drug and sandwiching between the films of the polymer. Two films of polymer containing drug were sealed by the polymer paste and sterilized by UV light. Glycerol was used as plasticizer.
Compatibility studies of the excipients and drug were checked by recording the FTIR spectra of the drug alone and in combination with other excipients. There was no major shifting of peaks were observed. Minor shifting of peaks were seen that do not show the change in the functional group. Peaks present at 2930 cm-1, 1762cm-1, 1689cm-1, 1215cm-1, 1072cm-1were shifted to 2935cm-1, 1766cm-1, 1608cm-1, 1242cm-1, 1068cm-1respectively. By comparing the spectra of Pilocarpine alone with that of formulation it was concluded that there was not any significant interaction between the components of the formulation and PN. The prepared ophthalmic inserts were checked for their physicochemical parameters. The surface pH of the ocular inserts was determined and found near to the pH of the lacrimal fluid. Sodium alginate did not cause any significant change in the pH due to its neutral nature (Rowe, Sheskey et al., 2006). The average pH of the prepared ocular insert was found 6.72 that was lower than the pH of lacrimal fluid i.e. 7.4 but still reasonable because the lacrimal fluid buffer capacity (Malhotra and Majumdar, 2001).
The thickness of ocular inserts was measured by using a digital micrometer and found between the range of 0.21mm (F3) to 0.32mm ( F4). The appropriate thickness of ophthalmic inserts minimized chances of ocular irritation. (Pawar, Katara et al., 2012). The thickness of the ocular inserts was directly proportional to the concentration of the polymer. The addition of the Sodium alginate also affected the thickness of the ocular inserts. Weight variation studies were also performed for the prepared ocular inserts and the maximum average weight was found 9.1mg for the formulation F4 while the lowest average weight was observed for the formulation F3 6.2mg. Different formulations showed different weights due to the use of the different concentrations of the polymer and addition of the Sodium Alginate but the ocuserts of the same formulations demonstrate the fair uniformity of the weight. Maximum average weight (9.1mg) was shown by the formulation F4 as highest concentration of the polymer was used in this formulation and minimum average was shown by the formulation F6 as minimum amount of the MKG was used in this formulation.
Swelling index was determined for ocuserts from six formulations and found that the maximum swelling index was for the formulation F4 that is 36.79 because maximum concentration of MKG was used in combination with Sodium Alginate in this formulation. The higher swelling index indicated the higher gel-forming ability of the polymer and better sustained effect (Rowe, Sheskey et al., 2006). Previously reported highest swelling index for the MKG was 34.95 so the addition of sodium alginate caused the increase in swelling index making it more suitable formulation for the sustained effect (Babu, Prasad et al., 2002).
Percentage of the drug contents was calculated to find out the uniformity of the Pilocarpine in the formulation. The results were found between 95.4 to 100.1 percent that complies with the requirements. This uniformity represents the accuracy and reproducibility of the method used to prepared ocular inserts (Williams, Adams et al., 2002).
The dissolution is the most common technique adopted to determine the release of drug from solid dosage forms (Uddin, Saffoon et al., 2011). In-vitro dissolution studies were performed for six formulations to determine the release profiles. Buffer (Phosphate buffer saline) of pH 7.4 was employed as a dissolution medium. The dissolution profiles for six formulations were found within satisfactory limit 69.2 ±1.36% to 90.5 ± 3.21% over the 12 hours. Dissolutions results showed that the formulations containing Sodium Alginate in combination of MKG illustrate more sustained release of drug as compared to the formulations containing MKG alone. Maximum sustained release of the drug (69.2±1.36%) was found from the formulation F4 which contains MKG (600mg) and Sodium alginate (0.5mg) and lowest drug retarding effect was found in formulation F3 which contains MKG (400mg) alone. Rate of release of drug was observed to be decreased with increase in the amount of the MKG so it was in an inverse relationship of polymer quantity and release rate of drug.
Drug release profiles meet pharmacopoeial requirements in which sustained released formulations must have the release profile more than 10 hours (USP, 2011). Dissolutions profiles of prepared ocular inserts reflect the fact that the addition of Sodium Alginate in the formulations cause a potential increase in the sustained effect of the formulation (I??klan, Kur?un et al., 2010).
Dissolution data were undergone through different Kinetic models. The optimized formulation F4 was found to be best follow the Korsmeyer peppas model by showing highest value of coefficient of correlation R2 = 0.9975. The value of "n" shows that how drug release from the dosage form. If the value n = 0.5 or less it shows Fickian diffusion, if n ranges from 0.5-1, shows that release pattern is non Fickian diffusion, value n=1 follows case II transport and value n more than 1 follows super case II transport (Lokhandwala, Deshpande et al., 2013). The value of “n” for formulation F4 was 0.672 illustrating the Non-Fickian diffusion mechanism.
Conclusion
MKG was found to be good release retarding polymer. The physicochemical characteristic and micrometric properties were seen to be in acceptable limits indicating the application of MKG for the development of ocuserts. Combination of MKG with sodium alginate as copolymer produced ocuserts of Pilocarpine nitrate. Ocuserts of PN were prepared successfully using MKG and SA at optimized concentrations (F4) The dissolution profiles of different formulations demonstrated that the MKG showed the release of drug up to 12 hours while the formulation (F4) containing SA in combination to MKG showed more sustained effect up to 69.2 ± 1.36 over the period of 12 hours.. In conclusion the results of the study suggested a potential use of MKG based ocuserts for sustained release of PN for the treatment of glaucoma.
References
- Amar A, Ashish K, Ajaykumar P. Anand JJIJoP (2012). Formulation and evaluation of controlled release ocular inserts of betaxolol hydrochloride. 3(5) 34-38.
- Anumolu K, Vijay Amritharaj R, Aleti SR. Kumar NS(2012) Analytical Evaluation Of Formulated Occular Nanoasuspension Of Pilocarpine Nitrate. International Journal Of Research In Pharmacy And Chemistry www.ijrpc.com
- Babu GMM, Prasad CD. Murthy KRJIjop (2002). Evaluation of modified gum karaya as carrier for the dissolution enhancement of poorly water- soluble drug nimodipine. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 234(1-2) 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(01)00925-5
- Breeveld A, Landsman W, Holland S, Roming P, Kuin N. Page M (2011). An updated ultraviolet calibration for the Swift/UVOT. AIP Conference Proceedings, AIP. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3621807
- Desai KG. Park HJJDd (2006). Study of gamma- irradiation effects on chitosan microparticles. 13(1) 39-50.
- Devhadrao N, Siddhaia MJJoDD. Therapeutics (2018). Review On Ocular Insert Drug Delivery System. 8(5-s) 115-121
- Endo T, Nakajima M, Fukami T, Hara Y, Hasunuma T, Yokoi T, Momose YJP. genomics (2008). Genetic polymorphisms of CYP2A6 affect the in- vivo pharmacokinetics of pilocarpine. 18(9) 761- 772.
- Europy R, Medicines EDftQo. Healthcare (2013). European Pharmacopoeia 8.0: Published in Accordance with the Convention on the Elaboration of a European Pharmacopoeia: European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Healthcare, Council of …
- Gupta S. VYAS SJSp (2010). Carbopol/chitosan based pH triggered in situ gelling system for ocular delivery of timolol maleate. National library of medicinee 78(4) 959-976. https://doi.org/10.3797/scipharm.1001-06
- Işıklan N, Kurşun F. İnal MJCp (2010). Graft copolymerization of itaconic acid onto sodium alginate using benzoyl peroxide. Carbohydrate Polymers 79(3) 665-672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.09.021
- Jain S, Yadav S, Patil UJRJoP. Technology (2008). Preparation and evaluation of sustained release matrix tablet of furosemide using natural polymers. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 1(4) 374-376. https://rjptonline.org/AbstractView.aspx?PID=2008-1-4-70
- Kabiri K, Omidian H, Hashemi S. Zohuriaan-Mehr MJEPJ (2003). Synthesis of fast-swelling superabsorbent hydrogels: effect of crosslinker type and concentration on porosity and absorption rate. Science Direct 39(7) 1341- 1348. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-3057(02)00391-9
- Krishnaiah Y, Reddy PB, Satyanarayana V. Karthikeyan RJIjop (2002). Studies on the development of oral colon targeted drug delivery systems for metronidazole in the treatment of amoebiasis. National Library of medicine 236(1-2) 43-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-5173(02)00006-6
- Kumari A, Sharma PK, Garg VK, Garg GJJoapt. research (2010). Ocular inserts—Advancement in therapy of eye diseases. National Library of medicine 1(3) 291. https://doi.org/10.4103%2F0110-5558.72419
- Lokhandwala H, Deshpande A. Deshpande SJIJPBS (2013). Kinetic modeling and dissolution profiles comparison: an overview. International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences 4(1):728-737 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288306223_Kinetic_modeling_and_dissolution_profiles_comparison_An_overview
- Malhotra M. Majumdar D (2001). Permeation through cornea. National Library of medicine 39(1):11-24. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11349520/
- Micard V, Belamri R, Morel M-H, Guilbert SJJoA. Chemistry F (2000). Properties of chemically and physically treated wheat gluten films. National library of medicine. 48(7) 2948-2953. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0001785
- Patel A, Cholkar K, Agrahari V. Mitra AKJWjop (2013). Ocular drug delivery systems: an overview. ational library of medicine. 2(2) 47. https://doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v2.i2.47
- Pawar PK, Katara R. Majumdar DKJAp (2012). Design and evaluation of moxifloxacin hydrochloride ocular insert. National library of medicine. 62(1) 93-104. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10007-012-0002-5
- Prajapati VD, Jani GK, Moradiya NG. Randeria NPJCp (2013). Pharmaceutical applications of various natural gums, mucilages and their modified forms. Science Direct 92(2) 1685-1699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.11.021
- Rathore K. Nema RJIJPR (2009a). Review on ocular inserts . International Journal of PharmTech Research 1(2) 164-169. https://sphinxsai.com/pdf/jpt_ap_ju_09/pt=10%20%20%20kamal%20rathore%20%20(164- 169).pdf
- Rathore K. Nema RJIJPSDR (2009b). An insight into ophthalmic drug delivery system. International Journal of pharmaceutical Sciences and drig research 1(1) 1-5. https://doi.org/10.25004/IJPSDR.2009.010101
- Reddy MM, Reddy JD, Moin A. Shivakumar HJTJoPR (2012). Formulation of sustained-release matrix tablets using cross-linked karaya gum. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 11(1) 28-35. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v11i1.4
- Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ. Owen SC (2006). Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients: Pharmaceutical press London
- Siepmann J. Peppas NJPR (2000). Hydrophilic matrices for controlled drug delivery: an improved mathematical model to predict the resulting drug release kinetics (the “sequential layer†model). National library of Medicine.17(10) 1290-1298. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1026455822595
- Sultana Y, Jain R, Aqil M. Ali AJCdd (2006). Review of ocular drug delivery. National library of Medicine. 3(2) 207-217. https://doi.org/10.2174/156720106776359186
- Uddin R, Saffoon N. Sutradhar KBJIJCBPR (2011). Dissolution and dissolution apparatus: a review. 1(4) 201-207. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262296435_Dissolution_and_Dissolution_Apparatus _A_Review
- SP UP (2011). 34, NF 29. The United States pharmacopeia and the National formulary. The United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Rockwille, MD.
- Vyas SP. Khar RK (2004). Targeted & controlled drug delivery: Novel carrier systems: CBS publishers & distributors.
- Williams RL, Adams WP, Poochikian G. Hauck WWJPr (2002). Content uniformity and dose uniformity: current approaches, statistical analyses, and presentation of an alternative approach, with special reference to oral inhalation and nasal drug products. 19(4) 359- 366. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1015114821387
- Amar A, Ashish K, Ajaykumar P. Anand JJIJoP (2012). Formulation and evaluation of controlled release ocular inserts of betaxolol hydrochloride. 3(5) 34-38.
- Anumolu K, Vijay Amritharaj R, Aleti SR. Kumar NS(2012) Analytical Evaluation Of Formulated Occular Nanoasuspension Of Pilocarpine Nitrate. International Journal Of Research In Pharmacy And Chemistry www.ijrpc.com
- Babu GMM, Prasad CD. Murthy KRJIjop (2002). Evaluation of modified gum karaya as carrier for the dissolution enhancement of poorly water- soluble drug nimodipine. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 234(1-2) 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(01)00925-5
- Breeveld A, Landsman W, Holland S, Roming P, Kuin N. Page M (2011). An updated ultraviolet calibration for the Swift/UVOT. AIP Conference Proceedings, AIP. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3621807
- Desai KG. Park HJJDd (2006). Study of gamma- irradiation effects on chitosan microparticles. 13(1) 39-50.
- Devhadrao N, Siddhaia MJJoDD. Therapeutics (2018). Review On Ocular Insert Drug Delivery System. 8(5-s) 115-121
- Endo T, Nakajima M, Fukami T, Hara Y, Hasunuma T, Yokoi T, Momose YJP. genomics (2008). Genetic polymorphisms of CYP2A6 affect the in- vivo pharmacokinetics of pilocarpine. 18(9) 761- 772.
- Europy R, Medicines EDftQo. Healthcare (2013). European Pharmacopoeia 8.0: Published in Accordance with the Convention on the Elaboration of a European Pharmacopoeia: European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Healthcare, Council of …
- Gupta S. VYAS SJSp (2010). Carbopol/chitosan based pH triggered in situ gelling system for ocular delivery of timolol maleate. National library of medicinee 78(4) 959-976. https://doi.org/10.3797/scipharm.1001-06
- Işıklan N, Kurşun F. İnal MJCp (2010). Graft copolymerization of itaconic acid onto sodium alginate using benzoyl peroxide. Carbohydrate Polymers 79(3) 665-672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.09.021
- Jain S, Yadav S, Patil UJRJoP. Technology (2008). Preparation and evaluation of sustained release matrix tablet of furosemide using natural polymers. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 1(4) 374-376. https://rjptonline.org/AbstractView.aspx?PID=2008-1-4-70
- Kabiri K, Omidian H, Hashemi S. Zohuriaan-Mehr MJEPJ (2003). Synthesis of fast-swelling superabsorbent hydrogels: effect of crosslinker type and concentration on porosity and absorption rate. Science Direct 39(7) 1341- 1348. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-3057(02)00391-9
- Krishnaiah Y, Reddy PB, Satyanarayana V. Karthikeyan RJIjop (2002). Studies on the development of oral colon targeted drug delivery systems for metronidazole in the treatment of amoebiasis. National Library of medicine 236(1-2) 43-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-5173(02)00006-6
- Kumari A, Sharma PK, Garg VK, Garg GJJoapt. research (2010). Ocular inserts—Advancement in therapy of eye diseases. National Library of medicine 1(3) 291. https://doi.org/10.4103%2F0110-5558.72419
- Lokhandwala H, Deshpande A. Deshpande SJIJPBS (2013). Kinetic modeling and dissolution profiles comparison: an overview. International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences 4(1):728-737 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288306223_Kinetic_modeling_and_dissolution_profiles_comparison_An_overview
- Malhotra M. Majumdar D (2001). Permeation through cornea. National Library of medicine 39(1):11-24. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11349520/
- Micard V, Belamri R, Morel M-H, Guilbert SJJoA. Chemistry F (2000). Properties of chemically and physically treated wheat gluten films. National library of medicine. 48(7) 2948-2953. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0001785
- Patel A, Cholkar K, Agrahari V. Mitra AKJWjop (2013). Ocular drug delivery systems: an overview. ational library of medicine. 2(2) 47. https://doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v2.i2.47
- Pawar PK, Katara R. Majumdar DKJAp (2012). Design and evaluation of moxifloxacin hydrochloride ocular insert. National library of medicine. 62(1) 93-104. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10007-012-0002-5
- Prajapati VD, Jani GK, Moradiya NG. Randeria NPJCp (2013). Pharmaceutical applications of various natural gums, mucilages and their modified forms. Science Direct 92(2) 1685-1699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.11.021
- Rathore K. Nema RJIJPR (2009a). Review on ocular inserts . International Journal of PharmTech Research 1(2) 164-169. https://sphinxsai.com/pdf/jpt_ap_ju_09/pt=10%20%20%20kamal%20rathore%20%20(164- 169).pdf
- Rathore K. Nema RJIJPSDR (2009b). An insight into ophthalmic drug delivery system. International Journal of pharmaceutical Sciences and drig research 1(1) 1-5. https://doi.org/10.25004/IJPSDR.2009.010101
- Reddy MM, Reddy JD, Moin A. Shivakumar HJTJoPR (2012). Formulation of sustained-release matrix tablets using cross-linked karaya gum. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 11(1) 28-35. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v11i1.4
- Rowe RC, Sheskey PJ. Owen SC (2006). Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients: Pharmaceutical press London
- Siepmann J. Peppas NJPR (2000). Hydrophilic matrices for controlled drug delivery: an improved mathematical model to predict the resulting drug release kinetics (the “sequential layer†model). National library of Medicine.17(10) 1290-1298. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1026455822595
- Sultana Y, Jain R, Aqil M. Ali AJCdd (2006). Review of ocular drug delivery. National library of Medicine. 3(2) 207-217. https://doi.org/10.2174/156720106776359186
- Uddin R, Saffoon N. Sutradhar KBJIJCBPR (2011). Dissolution and dissolution apparatus: a review. 1(4) 201-207. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262296435_Dissolution_and_Dissolution_Apparatus _A_Review
- SP UP (2011). 34, NF 29. The United States pharmacopeia and the National formulary. The United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Rockwille, MD.
- Vyas SP. Khar RK (2004). Targeted & controlled drug delivery: Novel carrier systems: CBS publishers & distributors.
- Williams RL, Adams WP, Poochikian G. Hauck WWJPr (2002). Content uniformity and dose uniformity: current approaches, statistical analyses, and presentation of an alternative approach, with special reference to oral inhalation and nasal drug products. 19(4) 359- 366. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1015114821387
Cite this article
-
APA : Shareef, S., Khan, M. I., & Sohail, M. F. (2022). Formulation and In-Vitro Evaluation of Sustained Release Pilocarpine Ocuserts Using Modified Karaya Gum Extracted from Sterculia urens. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VII(I), 28-40. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2022(VII-I).05
-
CHICAGO : Shareef, Sajida, Muhammad Imran Khan, and Muhammad Farhan Sohail. 2022. "Formulation and In-Vitro Evaluation of Sustained Release Pilocarpine Ocuserts Using Modified Karaya Gum Extracted from Sterculia urens." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VII (I): 28-40 doi: 10.31703/gpsr.2022(VII-I).05
-
HARVARD : SHAREEF, S., KHAN, M. I. & SOHAIL, M. F. 2022. Formulation and In-Vitro Evaluation of Sustained Release Pilocarpine Ocuserts Using Modified Karaya Gum Extracted from Sterculia urens. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VII, 28-40.
-
MHRA : Shareef, Sajida, Muhammad Imran Khan, and Muhammad Farhan Sohail. 2022. "Formulation and In-Vitro Evaluation of Sustained Release Pilocarpine Ocuserts Using Modified Karaya Gum Extracted from Sterculia urens." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VII: 28-40
-
MLA : Shareef, Sajida, Muhammad Imran Khan, and Muhammad Farhan Sohail. "Formulation and In-Vitro Evaluation of Sustained Release Pilocarpine Ocuserts Using Modified Karaya Gum Extracted from Sterculia urens." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VII.I (2022): 28-40 Print.
-
OXFORD : Shareef, Sajida, Khan, Muhammad Imran, and Sohail, Muhammad Farhan (2022), "Formulation and In-Vitro Evaluation of Sustained Release Pilocarpine Ocuserts Using Modified Karaya Gum Extracted from Sterculia urens", Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VII (I), 28-40
-
TURABIAN : Shareef, Sajida, Muhammad Imran Khan, and Muhammad Farhan Sohail. "Formulation and In-Vitro Evaluation of Sustained Release Pilocarpine Ocuserts Using Modified Karaya Gum Extracted from Sterculia urens." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review VII, no. I (2022): 28-40. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2022(VII-I).05
