02 Pages : 6-16
Abstrict
The aim of the present study was to develop bilayer sustained release tablets of to improve patient compliance of two drugs, tramadol and paracetamol. Immediate release layer contained both drugs tramadol hydrochloride and acetaminophen while the sustained release layer was designed only for the tramadol hydrochloride. Hydrophobic polymers Eudragit L-100, Eudragit S-100 and hydrophilic polymer hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose (HPMC K15), and wet granulation technique to produce bilayer matrix tablets. FTIR studies revealed no incompatibility among the ingredients. Out of 16 trials developed and characterized for weight variation, thickness, diameter, hardness, and friability, F16 showed promising result with immediate layer releasing drug 29% in 2 hours followed by sustained release 77% drug over 12 hours and followed zero order release. Therefore, bilayer sustained release tablets of tramadol with simultaneous loading of Paracetamol can be developed using Eudragit S-100 and hydroxyl propyl methylcellulose (HPMC K15) at equimolar content levels.
Keywords
Tramadol, Acetaminophen, Eudragit, HPMC K15, Bilayer, Sustained Release
Introduction
Tramadol hydrochloride (TRM) is a synthetic opioid, used to treat moderate to severe pain. It exists as a racemic mixture that play an important role owing to its analgesic activity by complementing each other (Brayfield, 2014). TRM is rapidly absorbed taking 1.6 h to reach peak plasma concentration (Cmax), while 20% plasma protein binding and extensively metabolized by liver. It has elimination half-life of about 6 h and is majorly excreted through the kidneys after oral administration (Scott & Perry, 2000). Most common side effects associated with tramadol hydrochloride are nausea, vomiting, agitation, pruritus, tremor, anxiety, constipation, hallucination and diaphoresis (Cossmann & Wilsmann, 1987).
Acetaminophen (AMP) is a NSAID drug having potent analgesic and antipyretic activity but possesses a weak anti-inflammatory activity. Acetaminophen inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins by replacing arachidonic acid for COX system (Botting, 2000). Acetaminophen is well absorbed and shows peak plasma concentration within 30-60 min, its plasma protein binding is about 25%, metabolized in the liver to form acetaminophen sulphate, acetaminophen glucuronide and N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone and excreted in the urine (Ward & Alexander-Williams, 1999).
Pharmaceutical industry is focusing on development of combination therapy that contains more than one active pharmaceutical ingredient in a single dosage form mostly as tablets. In order to avoid chemical incompatibilities between the active pharmaceutical ingredients by physical separation, bilayer tablet is a good option (Jayaprakash et al., 2011). Sequential drug release can be achieved using bilayer tablets carrying two drugs in combination through keeping two substances separate. Bilayer tablets can also serve as a sustained release tablet in which immediate release layer gives off an initial dose and sustained release layer sustains a maintenance dose (Skowyra et al., 2015). This strategy leads to reduced dose frequency and improved patient compliance (Mohammed et al., 2011).
In this study, a bilayer tablet system was designed for TRM and ACP as immediate outer layer and TRM sustained release core using varying proportions of Eudragit L-100, Eudragit S-100, PVP K30 and HPMC-K15. The as-prepared tablets were characterized and compared for different pharmaceutical parameters such as pre and post-compression parameters and drug release behavior.
Methodology
Materials
Tramadol hydrochloride and acetaminophen were obtained as gift samples from Highnoon Laboratories Lahore, Pakistan, and Unison Chemical Works Lahore, Pakistan. L-100 and Eudragit S-100 (Evonik, Germany). Polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP K30), Hydroxy propyl methylcellulose (HPMC K15), cross carmellose sodium, HCl and lactose were purchased from Merck, Germany, Magnesium stearate was procured from Fluka, Germany.
Pre-formulation studies
Pre-formulation is an essential step in coherent formulation of an active ingredient. Immediate release layer granules and sustained release layer granules were analyzed for following physical tests.
Bulk density
Accurately weighed amount (10g) of granules was taken and poured into a graduated cylinder with the help of a large funnel and volume in graduated cylinder was measured. The bulk density was recorded with the help of following formula as described (Abdullah & Geldart, 1999).
D_b=W_g/V
Here
Db = bulk density of granules,
Wg = weight of granules and
V = volume of granules.
Tapped Density
Tapped density of the granules was determined by tapping the graduated cylinder containing the granules previously used in the bulk density test. Volume of the tapped granules was measured after tapping as described (Abdullah & Geldart, 1999).
D_t=W_g/V_t
Here
Dt = tapped density of granules
Wg = weight of granules
Vt = volume of granules after tapping.
Hausner’s Ratio, Carr’s Index and, Angle of Repose
Hausner’s ration was calculated from tapped density (Dt) and bulk density (Db) by using the following formula (Sánchez et al., 1995).
H=D_t/D_b
Where Dt = tapped density of the granules and Db = bulk density of the granules.
Compressibility of granules is indicated by Carr’s index (CI). It is calculated by following formula as described (Shamma & Basha, 2013).
Angle of repose was calculated by dropping the granules from a funnel to form a heap and applying the following formula. (Stegner, 2000).
Where ? = angle of repose of the heap, h = height of heap and r = radius of heap.
Fourier Transformation Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
The possible interactions between drug – drug and drug – polymers were studied using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectrophotometer. Pure ingredients, physical mixtures and granules were evaluated using the FTIR (Shimadzu, Germany). Scanning was done in the range of 650-4000 cm-1 (Khanmohammadi et al., 2009).
Tablet Compression
Fabrication of Immediate and Sustained Release Granules
Granules for immediate release layer having TRM and ACP was prepared through wet granulation method using the ingredients as mentioned in Table 1. After weighing each ingredient accurately and separately, granules were prepared through wet granulation method (Atram et al., 2009). Immediate release layer was colored yellow to distinguish it from sustained release layer. Sustained release granules through wet granulation comprising TRM was prepared using different polymers concentrations as shown in Table 2.
Fabrication of Bilayer Tablet
300mg of granules of immediate release layer were added in the die cavity and pressed slightly. Then 200mg of sustained release layer granules were added on the slightly pressed immediate release layer in the die cavity of single punch compression machine (Emmy, Pakistan) and punched the tablets respectively (Gopinath et al., 2013).
Evaluation of Bilayer Tablets
Bilayer tablets were characterized for following parameters.
Weight Variation Test
Uniformity in weight of tablets was determined by weighing 20 tablets of each formulation trial, which were picked randomly using an analytical weighing balance (EMMAY enterprises). After that their percentage variation in weight was determined (Dunnett & Crisafio, 1955).
Thickness and Diameter
Tablets were taken in the jaw of vernier caliper and measurements were recorded (EMMAY enterprises). A triplicate reading was taken of all formulations for thickness and diameter.
Hardness Test
Monsanto hardness tester (EMMAY enterprises) was used to determine the tablet hardness. Five tablets from each formulation were selected randomly to determine the hardness (KITAZAWA et al., 1975).
Friability Test
Friability of the tablets was determined using Roche
friabilator (Roche, Switzerland). 10 tablets were selected randomly, weighed and then placed in the chamber of the friability apparatus. The apparatus was run at a speed of 25rpm for 4 min. Tablets were removed from the chamber and then weighed collectively. Following equation was used to determine percent friability as described (Henry, 1961).
Here W1 = weight of tablets before test and W2= weight of tablets after test.
Dissolution Studies
USP type II dissolution apparatus (Galvano Scientific, Pakistan) was employed dissolution analysis of the bilayer tablet. The release study was performed in 900 mL of 0.1 N HCl maintained at 37± 0.5? and 50 rpm. At pre-defined intervals, samples were taken to determine the release profile of drugs in the immediate release layer. After two hours, dissolution study was carried out in pH 6.8 carrying the sustained release layer. Samples were taken at 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12 hrs. All samples were analyzed at 272nm for TRM and at 257nm for ACP respectively using a UV-Visible spectrophotometer (T70UV/VIS PG instrument, SHIMADZU, Germany). All the tests were run in triplicate and the average of three formulations was calculated (Reddy et al., 2003). The release data was subjected to different kinetic models using the DD Solver (a free Microsoft Add in) (Shamma & Basha, 2013).
Results
Bilayer tablets are used to deliver both loading and maintenance dose of same or different drug. The development of cheap, effective and multipurpose tablet would be beneficial in terms of pharmacoeconomics. Bilayer tablets having TRM and ACP were successfully prepared according to the ratios in Table 1 and 2.
Table 1. Fabrication of Immediate Release Layer of Tramadol Hydrochloride and Acetaminophen Containing Different Binders and Excipients.
|
S. No |
Name of ingredient |
Weight (mg) |
|
1 |
Tramadol Hydrochloride |
50 |
|
2 |
Acetaminophen |
100 |
|
3 |
Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone (PVP
K30) |
5 |
|
4 |
Cross carmellose Sodium |
15 |
|
5 |
Lactose |
125 |
|
6 |
Magnesium stearate |
5 |
|
|
Total |
300 |
Table
2. Composition of Sustained
Release Layer Formulations of Bilayer Tablets Containing Different
Concentrations of Eudragit L-100, Eudragit S-100 and HPMC
|
Formulation |
Eudragit
L-100 (mg) |
Eudragit S-100 (mg) |
HPMC K15 (mg) |
Lactose (mg) |
Tramadol HCl
(mg) |
Magnesium Stearate (mg) |
|
F1 |
40 |
- |
10 |
46 |
100 |
4 |
|
F2 |
40 |
- |
20 |
36 |
100 |
4 |
|
F3 |
40 |
- |
30 |
26 |
100 |
4 |
|
F4 |
40 |
- |
40 |
16 |
100 |
4 |
|
F5 |
10 |
- |
40 |
46 |
100 |
4 |
|
F6 |
20 |
- |
40 |
36 |
100 |
4 |
|
F7 |
30 |
- |
40 |
26 |
100 |
4 |
|
F8 |
40 |
- |
40 |
16 |
100 |
4 |
|
F9 |
- |
40 |
10 |
46 |
100 |
4 |
|
F10 |
- |
40 |
20 |
36 |
100 |
4 |
|
F11 |
- |
40 |
30 |
26 |
100 |
4 |
|
F12 |
- |
40 |
40 |
16 |
100 |
4 |
|
F13 |
- |
10 |
40 |
46 |
100 |
4 |
|
F14 |
- |
20 |
40 |
36 |
100 |
4 |
|
F15 |
- |
30 |
40 |
26 |
100 |
4 |
|
F16 |
- |
40 |
40 |
16 |
100 |
4 |
Pre-compression Studies
Pre-Compression Studies of Immediate Release Granules
Pre-compression studies were performed for immediate release granules having TRM and ACP mixed with
Excipients and processed through wet granulation. The result of different parameters such as bulk density, tapped density, Hausner’s ratio, Carr’s index and angle of repose are shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Pre-Compression Studies (Bulk Density, Tapped Density, Hausner’s Ratio, Carr’s Index and Angle of Repose) for Granules of Immediate Release Layer
|
Formulation
|
Bulk
Density(g/ml) |
Tapped
Density (g/ml) |
Hausner’s
Ratio |
Carr’s
Index (%) |
Angle
of repose (?) |
|
Immediate
release layer |
0.80 |
0.92 |
1.15 |
13.04 |
25.69 |
The results of pre-compression study obtained from bulk density studies of granules for sustained release
layer of bilayer matrix tablets is shown in Fig 1.

formulation studies of sustained
release layer (A) Bulk density (B) Tapped density (C) Hausner’s ratio (D)
Carr’s Index
Post–Compression Studies
The tablets prepared in this study were analyzed by different quality control tests as following.
Weight Variation, Hardness and Thickness
Tablets were analyzed by following the United State Pharmacopoeia protocol i.e. tablets weighing 324 mg were accepted with ± 5 weight variation. Results of post-compression parameters (mean±standard deviation) of the tablets is showed in the Fig 2 (Shiyani et al., 2008).

Figure 2: Post
formulation studies of sustained release layer (A) Weight variation (B)
Thickness (C) Hardness.
FTIR Studies
To ensure the safety of formulation, the possibility of any interactions among the ingredients was evaluated through FTIR analysis. The results of various FTIR spectra recorded are shown in Fig 3.
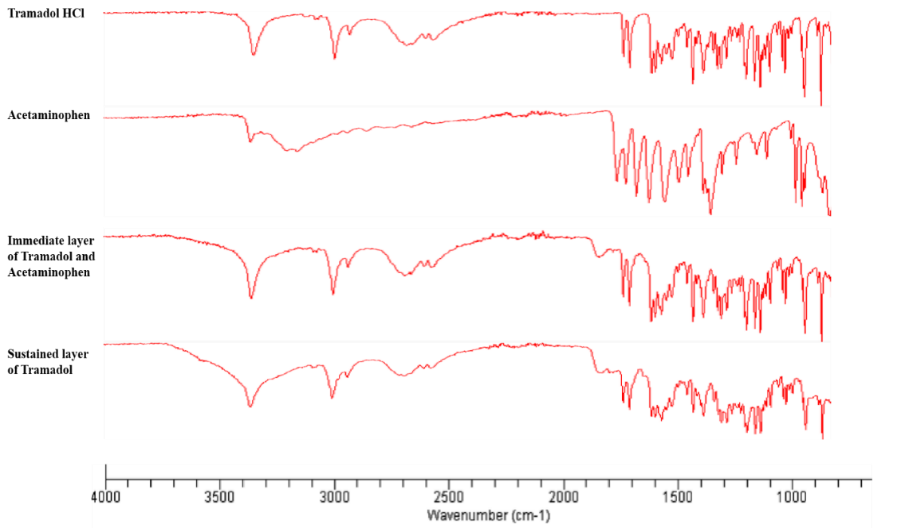
Figure 3
Figure 3. FTIR
spectra of tramadol HCl, Acetaminophen, immediate layer of Tramadol and
Acetaminophen, Sustained layer of Tramadol by using FTIR (Shimadzu, Germany).
Scanning was done in the range of 650-4000 cm-1
Drug Release Studies
The dissolution studies provide an insight on release behavior of the drug from a formulation. It provides us an idea about the effect of formualtion variables
Which govern the release profile. Drug release profiles of sustained release layers of formulations labelled (F1-F7) and F9-F16 are depicted in figure 4 & 5.

Figure 4: Dissolution studies of sustained release layers of
formulations (F1-F7) in Acidic medium 0.1N HCL at 1.2 pH
for 2 hours then in phosphate buffer at pH6.8 up to 12 hours at wavelength of
272nm for tramadol and at 257nm of acetaminophen

Figure 5
Figure 5: Dissolution studies of sustained release layers of formulations
(F9-F16) in Acidic medium 0.1N HCL at 1.2 pH for 2 hours
then in phosphate buffer at pH6.8 up to 12 hours at wavelength of 272nm for
tramadol and at 257nm of acetaminophen
Discussion
Polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP K30) and Croscarmellose sodium were chosen as excipients in tablet formulations.
PVP K30 is widely used in pharmaceutical research to sustain the release of drugs and prevent crystal formation owing to high glass transition temperature (Frizon et al., 2013). Existence of layers from different polymers, make a compartment for both bolus and controlled release of drug (Kale et al., 2011).
Bulk density of a powder represents packing of the powder particle in its bulk form and changes as the powder particles are made to consolidate by application of stress e.g., tapping the powder. A tapped powder possesses greater arch strength than a less consolidated one. Bulk density of immediate release granules was 0.80g/ml whereas tapped density was 0.91g/ml. These values of bulk density indicate good packing behavior (Mužíková & Nováková, 2007). The bulk volume can be reduced by tapping or mechanical pressure to remove voids and spaces and tapped density can be evaluated. The results of Hausner’s ratio and Carr’s index were also depicted good flow properties of granules. The angle of repose values suggested desirable flow properties. Previously, similar studies have shown that granules prepared with polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP K30), lactose and cross carmellose sodium have desirable angle of repose (Hlinak et al., 2006).
The results revealed that the inter-formulation variability was minimum for formulations F1-F4 as concentration of HPMC K15 is increased. Formulation (F5) showed highest bulk density as compared to all other formulations. As concentration of Eudragit L-100 was increased (F1-F8) and HPMC K15 remained constant, bulk density decreased slightly as shown in Fig 1. By addition of polymer Eudragit S-100 and decreasing concentration of HPMC K15 (F9-F12), there was not any substantial difference in bulk density. In case of formulations (F13-F16), bulk density decreased with increasing concentration of Eudragit S-100. The overall values of bulk density decreased as concentrations of polymers increased. It might be due to increased particle size and free flowing granules. It rendered granules low-weight, ultimately increasing floating ability of tablets in stomach (Albhar et al., 2012). These polymers have been extensively investigated for their swelling properties as well as capability to form hydro colloid systems. When they contact with water, form hydrogel layer act as a gel boundary for the delivery system, hence low density granules can float easily (Narendra et al., 2006). The flow properties play a vital role in transferring materials from container and processing to ensure the content uniformity and preventing weight variation. Hausner’s ratio and Carr’s index are calculated to determine the flow properties of materials. The Hausner’s and Carr’s index of all formulations were within range of 1.13-1.40 and 11.11 – 29.63 respectively showing excellent flow properties as shown in Fig 1 (Weitzel, 2012).
Hardness is the second most important physical characteristic that effects handeling, transportation and also disintegration of the tablets. It indicates the ability of a tablet to withstand mechanical shocks during handling (Nguyen et al., 2015). Maximum hardness was observed for formulation F9, which might be due to higher concentration of Eudragit S-100. Eudragit S-100 belongs to acrylic resins, acting as a bio-adhesive polymer resulting into increased tablet hardness (Kadian & Harikumar, 2016). Tablet thickness is another important parameter for quality control of tablets. It indicates the consistency of appearance of tablets. Tablet thickness was varied within range of 5.5 mm to 6.2 mm. Minimum thickness was measured for formulation F12 and maximum thickness was observed with formulation F11 and F16 as shown in Fig 2.
TRM and ACP containing tablet and pure materials (TRM and ACP) showed identical spectrograms. Aromatic ring that stretches at 1600 cm-1, aliphatic stretching at 2900 cm-1, aromatic CH stretching at 3050 cm-1 and shoulders of OH at 3300 cm-1. Absence of any new peaks in the FTIR spectrograms, therefore, suggested that lack of chemical or physical interactions between drug and excipients used in the formulation.
Drug release profile of formulations (F1- F4) of bilayer tablets having a constant ratio of Eudragit L-100 and varying hydroxy propyl methylcellulose (HPMC K15) ratio were evaluated. The drug release from the matrix tablets is decreased as the proportion of polymer hydroxy propyl methylcellulose (HPMC K15) was increased from 5% - 20%. Maximum retarded release rate was observed for formulation (F4) when both the polymers were kept at equimolar ratio of 20%. Drug release profile of formulation (F1) demonstrated 98% of drug release within 12 hours compared to formulation (F4) which showed cumulative release of 79% within the same time period Fig 4. Drug release profile of formulations (F5, F6, F7 & F8) of bilayer tablet formulations having a varying concentration of Eudragit L-100 and constant hydroxy propyl methylcellulose (HPMC K15) ratio is given in Fig 4. The drug release from the matrix tablets is regarded as the amount of polymer Eudragit L100 is increased from 5% - 20% in formulation F5 –F8 keeping the hydroxy propyl methylcellulose (HPMC K15) amount constant to 20%. Maximum retardness in release was seen for formulation F8 when both the polymers were in an equal amount. As concentration of polymer was increased by keeping one polymer constant respectively, it caused the release more sustained. These polymers acted as barriers and offered more sustained release. The formulation containing higher concentration of polymer provided t release 79% up to 12 hours.
Drug release profile of formulations (F9, F10, F11 & F12) of bilayer tablets having a constant ratio of Eudragit S-100 and varying hydroxy propyl methylcellulose (HPMC K15) ratio is given in Fig 5. The drug release from the matrix tablets is decreased as the amount of polymer hydroxy propyl methylcellulose (HPMC K15) increased from 5% - 20% in F1 – F4 keeping the Eudragit S-100 amount constant to 20%. Maximum decrease in release rate was seen for F12 when both the polymers were in an equal amount of 20%. Drug release data reveals that 100% of drug was released within 12 hours for F9. The release of drug from matrix tablets was decreased to 77.92% in F12.
Drug release profiles of formulations (F13, F14, F15 and F16) of bilayer tablet formulations having a varying concentration of Eudragit S-100 and constant hydroxy propyl methylcellulose (HPMC K15) ratio is given in Fig 5. The drug release from the matrix tablets is decreased as the amount of polymer Eudragit L100 is increased from 5% - 20% in formulation (F13 –F16) keeping the hydroxy propyl methylcellulose (HPMC K15) amount constant to 20%. Maximum slow-release rate was seen for formulation F16 when both the polymers were in an equal concentration. Higher concentration of Eudragit S100 is previously reported to prevented the penetration of aqueous media into tablet in agreement with our findings (SWAIN et al., 2016). Diffusion is the predominant release mechanism for most of the matrix drug delivery systems. Diffusion controlled release of the drug can be sustained by preventing penetration of the aqueous media intro the drug delivery systems; a strategy that is mostly used in designing sustained release tablets. (Asane et al., 2008). HPMC K15 is hydrophilic polymer and widely used in designing sustained release tablets, it act as barrier and controlled the release up to 12 hours (Dudhat, 2013). Kinetic analysis of drug release was done by fitting data into zero order model, first order model and Higuchi’s model. After calculation of regression coefficient (R2) values, it was observed that formulation F16 exhibited zero order release kinetics. The Maximum value for regression coefficient (R2) for zero order release kinetics was observed for formulation F16 (0.991). These findings revealed that the drug release from bilayer matrix tablets is sustained and independent of the initial drug concentration.
Conclusion
Various hydrophobic polymers Eudragit L-100 and Eudragit S-100 and hydrophilic polymer hydroxy propyl methylcellulose (HPMC K15) were used as drug release retardants, using wet granulation technique. Different pre- and post-compression parameters suggested that tablets were acceptable for pharmaceutical applications. The in vitro dissolution studies demonstrated sustained release of drug from the tablets as a function of polymer concentration. Maximum decrease in drug release was seen for formulation F16 (63.64%) with in 12hrs. F16 exhibited approximate zero order drug drug release. The overall results indicated promising potential of prepared bilayer tablets as an alternative to conventional dosage form.
References
- Abdullah, E., & Geldart, D. (1999). The use of bulk density measurements as flowability indicators. Powder technology, 102(2), 151-165
- Albhar, K. G., Wagh, V. S., & Chavan, B. (2012). Effect of HPMC K4M, HPMC K15M, sodium alginate and carbopol 934 in the formulation of carbonyl iron capsule. J Der Pharm Lett, 4(1), 94-367.
- Asane, G., Nirmal, S., Rasal, K., Naik, A., Mahadik, M., & Rao, Y. M. (2008). Polymers for mucoadhesive drug delivery system: a current status. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 34(11), 1246-1266.
- Atram, S., Udavant, Y., Salunke, R., Neb, G., Shahi, S., Gulecha, B., & Padalkar, A. (2009). Formulation of bilayer tablet containing metoprolol succinate and amlodipine besylate as a model drug for antihypertensive therapy. Journal of Pharmacy Research, 2(8), 1335- 1347.
- Botting, R. M. (2000). Mechanism of action of acetaminophen: is there a cyclooxygenase 3? Clinical Infectious Diseases, 31(Supplement_5), S202-S210.
- Brayfield, A. (2014). Tramadol hydrochloride. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. Pharmaceutical Press., 5.
- Cossmann, M., & Wilsmann, K. (1987). Effect and side effects of tramadol: an open phase IV study with 7198 patients. Therapiewoche, 37, 3475- 3485.
- Dudhat, K. R. (2013). Design and Development of Bilayer Tablets of Ondansetron Hydrochloride and Pantoprazole Sodium for Targeted Drug Delivery.
- Dunnett, C., & Crisafio, R. (1955). The operating characteristics of some official weight variation tests for tablets. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 7(1), 314-327.
- Frizon, F., de Oliveira Eloy, J., Donaduzzi, C. M., Mitsui, M. L., & Marchetti, J. M. (2013). Dissolution rate enhancement of loratadine in polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30 solid dispersions by solvent methods. Powder technology, 235, 532-539.
- Gopinath, C., Bindu, V. H., & Nischala, M. (2013). An overview on bilayered tablet technology. Journal of global trends in pharmaceutical sciences, 4(2), 1077-1085.
- Henry, B. R. (1961). Friable tablet and process for manufacturing same. In: Google Patents.
- Hlinak, A. J., Kuriyan, K., Morris, K. R., Reklaitis, G. V., & Basu, P. K. (2006). Understanding critical material properties for solid dosage form design. Journal of Pharmaceutical Innovation, 1(1), 12-17.
- Jayaprakash, S., Halith, S. M., Pillai, K. K., Balasubramaniyam, P., Firthouse, P. M., & Boopathi, M. (2011). Formulation and evaluation of bilayer tablets of amlodipine besilate and metprolol succinate. Der Pharmacia Lettre, 3(4), 143-154.
- Kadian, S. S., & Harikumar, S. (2016). Eudragit and its pharmaceutical significance. In
- Kale, S. S., Saste, V. S., Ughade, P. L., & Baviskar, D. T. (2011). Bilayer tablet. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research, 9(1), 25-30.
- Khanmohammadi, M., Garmarudi, A. B., Ghasemi, K., Jaliseh, H. K., & Kaviani, A. (2009). Diagnosis of colon cancer by attenuated total reflectance- fourier transform infrared microspectroscopy and soft independent modeling of class analogy. Medical Oncology, 26(3), 292-297.
- KITAZAWA, S., JOHNO, I., ITO, Y., TERAMURA, S., & OKADA, J. (1975). Effects of hardness on the disintegration time and the dissolution rate of uncoated caffeine tablets. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 27(10), 765-770.
- Mohammed, M., Maringanti, P. S., & Mamidi, S. (2011). Formulation and evaluation of bilayered tablets of montelukast and levocetrizine dihydrochloride using natural and synthetic polymers. International Journal of drug delivery, 3(4), 597.
- MužÃÂková, J., & Nováková, P. (2007). A study of the properties of compacts from silicified microcrystalline celluloses. Drug development and industrial pharmacy, 33(7), 775-781.
- Narendra, C., Srinath, M., & Babu, G. (2006). Optimization of bilayer floating tablet containing metoprolol tartrate as a model drug for gastric retention. AAPS PharmSciTech, 7(2), E23-E29.
- Nguyen, T. H., Morton, D., & Hapgood, K. (2015). Prediction of the tablet hardness: Exploration of microcrystalline cellulose and scale-up in wet granulation. Asia Pacific Confederation of Chemical Engineering Congress 2015: APCChE 2015, incorporating CHEMECA 2015,
- Reddy, K. R., Mutalik, S., & Reddy, S. (2003). Once- daily sustained-release matrix tablets of nicorandil: formulation and in vitro evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech, 4(4), 480-488.
- Sánchez, L., Torrado, S., & Lastres, J. (1995). Gelatinized/freeze-dried starch as excipient in sustained release tablets. International journal of pharmaceutics, 115(2), 201-208.
- Scott, L. J., & Perry, C. M. (2000). Tramadol. Drugs, 60(1), 139-176.
- Shamma, R. N., & Basha, M. (2013). Soluplus®: A novel polymeric solubilizer for optimization of Carvedilol solid dispersions: Formulation design and effect of method of preparation. Powder technology, 237, 406-414.
- Shiyani, B., Gattani, S., & Surana, S. (2008). Formulation and evaluation of bi-layer tablet of metoclopramide hydrochloride and ibuprofen. AAPS PharmSciTech, 9(3), 818-827.
- Skowyra, J., Pietrzak, K., & Alhnan, M. A. (2015). Fabrication of extended-release patient-tailored prednisolone tablets via fused deposition modelling (FDM) 3D printing. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 68, 11-17.
- Stegner, W. (2000). Angle of repose. Penguin.
- SWAIN, R. P., KUMARI, T. R., & PANDA, S. (2016). Formulation development and evaluation of sustained release ibuprofen tablets with acrylic polymers (Eudragit) and HPMC. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 8(2).
- Ward, B., & Alexander-Williams, J. M. (1999). Paracetamol revisited: a review of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Acute Pain, 2(3), 139-149.
- Weitzel, M. J. (2012). The estimation and use of measurement uncertainty for a drug substance test procedure validated according to USP
- Abdullah, E., & Geldart, D. (1999). The use of bulk density measurements as flowability indicators. Powder technology, 102(2), 151-165
- Albhar, K. G., Wagh, V. S., & Chavan, B. (2012). Effect of HPMC K4M, HPMC K15M, sodium alginate and carbopol 934 in the formulation of carbonyl iron capsule. J Der Pharm Lett, 4(1), 94-367.
- Asane, G., Nirmal, S., Rasal, K., Naik, A., Mahadik, M., & Rao, Y. M. (2008). Polymers for mucoadhesive drug delivery system: a current status. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 34(11), 1246-1266.
- Atram, S., Udavant, Y., Salunke, R., Neb, G., Shahi, S., Gulecha, B., & Padalkar, A. (2009). Formulation of bilayer tablet containing metoprolol succinate and amlodipine besylate as a model drug for antihypertensive therapy. Journal of Pharmacy Research, 2(8), 1335- 1347.
- Botting, R. M. (2000). Mechanism of action of acetaminophen: is there a cyclooxygenase 3? Clinical Infectious Diseases, 31(Supplement_5), S202-S210.
- Brayfield, A. (2014). Tramadol hydrochloride. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. Pharmaceutical Press., 5.
- Cossmann, M., & Wilsmann, K. (1987). Effect and side effects of tramadol: an open phase IV study with 7198 patients. Therapiewoche, 37, 3475- 3485.
- Dudhat, K. R. (2013). Design and Development of Bilayer Tablets of Ondansetron Hydrochloride and Pantoprazole Sodium for Targeted Drug Delivery.
- Dunnett, C., & Crisafio, R. (1955). The operating characteristics of some official weight variation tests for tablets. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 7(1), 314-327.
- Frizon, F., de Oliveira Eloy, J., Donaduzzi, C. M., Mitsui, M. L., & Marchetti, J. M. (2013). Dissolution rate enhancement of loratadine in polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30 solid dispersions by solvent methods. Powder technology, 235, 532-539.
- Gopinath, C., Bindu, V. H., & Nischala, M. (2013). An overview on bilayered tablet technology. Journal of global trends in pharmaceutical sciences, 4(2), 1077-1085.
- Henry, B. R. (1961). Friable tablet and process for manufacturing same. In: Google Patents.
- Hlinak, A. J., Kuriyan, K., Morris, K. R., Reklaitis, G. V., & Basu, P. K. (2006). Understanding critical material properties for solid dosage form design. Journal of Pharmaceutical Innovation, 1(1), 12-17.
- Jayaprakash, S., Halith, S. M., Pillai, K. K., Balasubramaniyam, P., Firthouse, P. M., & Boopathi, M. (2011). Formulation and evaluation of bilayer tablets of amlodipine besilate and metprolol succinate. Der Pharmacia Lettre, 3(4), 143-154.
- Kadian, S. S., & Harikumar, S. (2016). Eudragit and its pharmaceutical significance. In
- Kale, S. S., Saste, V. S., Ughade, P. L., & Baviskar, D. T. (2011). Bilayer tablet. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research, 9(1), 25-30.
- Khanmohammadi, M., Garmarudi, A. B., Ghasemi, K., Jaliseh, H. K., & Kaviani, A. (2009). Diagnosis of colon cancer by attenuated total reflectance- fourier transform infrared microspectroscopy and soft independent modeling of class analogy. Medical Oncology, 26(3), 292-297.
- KITAZAWA, S., JOHNO, I., ITO, Y., TERAMURA, S., & OKADA, J. (1975). Effects of hardness on the disintegration time and the dissolution rate of uncoated caffeine tablets. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 27(10), 765-770.
- Mohammed, M., Maringanti, P. S., & Mamidi, S. (2011). Formulation and evaluation of bilayered tablets of montelukast and levocetrizine dihydrochloride using natural and synthetic polymers. International Journal of drug delivery, 3(4), 597.
- MužÃÂková, J., & Nováková, P. (2007). A study of the properties of compacts from silicified microcrystalline celluloses. Drug development and industrial pharmacy, 33(7), 775-781.
- Narendra, C., Srinath, M., & Babu, G. (2006). Optimization of bilayer floating tablet containing metoprolol tartrate as a model drug for gastric retention. AAPS PharmSciTech, 7(2), E23-E29.
- Nguyen, T. H., Morton, D., & Hapgood, K. (2015). Prediction of the tablet hardness: Exploration of microcrystalline cellulose and scale-up in wet granulation. Asia Pacific Confederation of Chemical Engineering Congress 2015: APCChE 2015, incorporating CHEMECA 2015,
- Reddy, K. R., Mutalik, S., & Reddy, S. (2003). Once- daily sustained-release matrix tablets of nicorandil: formulation and in vitro evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech, 4(4), 480-488.
- Sánchez, L., Torrado, S., & Lastres, J. (1995). Gelatinized/freeze-dried starch as excipient in sustained release tablets. International journal of pharmaceutics, 115(2), 201-208.
- Scott, L. J., & Perry, C. M. (2000). Tramadol. Drugs, 60(1), 139-176.
- Shamma, R. N., & Basha, M. (2013). Soluplus®: A novel polymeric solubilizer for optimization of Carvedilol solid dispersions: Formulation design and effect of method of preparation. Powder technology, 237, 406-414.
- Shiyani, B., Gattani, S., & Surana, S. (2008). Formulation and evaluation of bi-layer tablet of metoclopramide hydrochloride and ibuprofen. AAPS PharmSciTech, 9(3), 818-827.
- Skowyra, J., Pietrzak, K., & Alhnan, M. A. (2015). Fabrication of extended-release patient-tailored prednisolone tablets via fused deposition modelling (FDM) 3D printing. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 68, 11-17.
- Stegner, W. (2000). Angle of repose. Penguin.
- SWAIN, R. P., KUMARI, T. R., & PANDA, S. (2016). Formulation development and evaluation of sustained release ibuprofen tablets with acrylic polymers (Eudragit) and HPMC. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 8(2).
- Ward, B., & Alexander-Williams, J. M. (1999). Paracetamol revisited: a review of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Acute Pain, 2(3), 139-149.
- Weitzel, M. J. (2012). The estimation and use of measurement uncertainty for a drug substance test procedure validated according to USP
Cite this article
-
APA : Javed, R., Ijaz, S., & Waqar, K. (2016). Development and Characterization of Bilayer Sustained Release Tablets of Tramadol HCl and Acetaminophen. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, I(I), 6-16. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2016(I-I).02
-
CHICAGO : Javed, Rashid, Sana Ijaz, and Kainat Waqar. 2016. "Development and Characterization of Bilayer Sustained Release Tablets of Tramadol HCl and Acetaminophen." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, I (I): 6-16 doi: 10.31703/gpsr.2016(I-I).02
-
HARVARD : JAVED, R., IJAZ, S. & WAQAR, K. 2016. Development and Characterization of Bilayer Sustained Release Tablets of Tramadol HCl and Acetaminophen. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, I, 6-16.
-
MHRA : Javed, Rashid, Sana Ijaz, and Kainat Waqar. 2016. "Development and Characterization of Bilayer Sustained Release Tablets of Tramadol HCl and Acetaminophen." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, I: 6-16
-
MLA : Javed, Rashid, Sana Ijaz, and Kainat Waqar. "Development and Characterization of Bilayer Sustained Release Tablets of Tramadol HCl and Acetaminophen." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, I.I (2016): 6-16 Print.
-
OXFORD : Javed, Rashid, Ijaz, Sana, and Waqar, Kainat (2016), "Development and Characterization of Bilayer Sustained Release Tablets of Tramadol HCl and Acetaminophen", Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, I (I), 6-16
-
TURABIAN : Javed, Rashid, Sana Ijaz, and Kainat Waqar. "Development and Characterization of Bilayer Sustained Release Tablets of Tramadol HCl and Acetaminophen." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review I, no. I (2016): 6-16. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2016(I-I).02
